Structures Of Abc Transporters In The Inward
Both ABCA5/8 and ABCA1 are members of the ATP-binding cassette or ABC family of transporters. These have a common structural organization. Several ABC transporters have been crystallized in the inward- and outward open conformations , and the two structures provide a glimpse of how they work.
ABC transporters often have rather broad substrate specificity and mediate the membrane translocation of many metabolites and xenobiotics. In addition to cholesterol and other membrane lipids, important examples are bile acids , conjugated bilirubin , drugs, and drug metabolites . Cancer cells often overexpress ABC transporters, which renders them resistant to multiple anticancer drugs.
11.4.6
Lipoid Cah And Cyp11a1 Defects
Failure of transmitochondrial cholesterol transport with secondary failure of initiation of steroidogenesis occurs with steroidogenic acute regulatory protein defects . Lipid accumulation in the cytoplasm with secondary destruction of adrenal cells lead to the disorder lipoid CAH. The expected clinical presentation in the 46, XY newborn with StAR protein defects caused by complete loss of function mutations is that of glucocorticoid deficiency, mineralocorticoid deficiency, and absence of virilization, with female-appearing external genitalia. There have been descriptions of what appears to be a milder or nonclassical form of lipoid CAH in which the onset and severity of adrenal insufficiency and gonadal failure may be variable.
Mutations in CYP11A1 , which encodes the cytochrome P450 side chain cleavage enzyme, catalyze the conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone, an early step in adrenal steroidogenesis, and result in a clinical picture of glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid deficiency and disorder of sexual development similar to that of lipoid CAH depending on the severity of enzymatic deficiency there is a wide phenotypic spectrum. Adrenal imaging may represent an important clinical pearl in differentiating lipoid CAH from side chain cleavage enzyme deficiency by visualizing enlarged versus small adrenal glands, respectively.86,8892
T. Else, G.D. Hammer, in, 2007
Hdl Transport From Plasma To Lymph
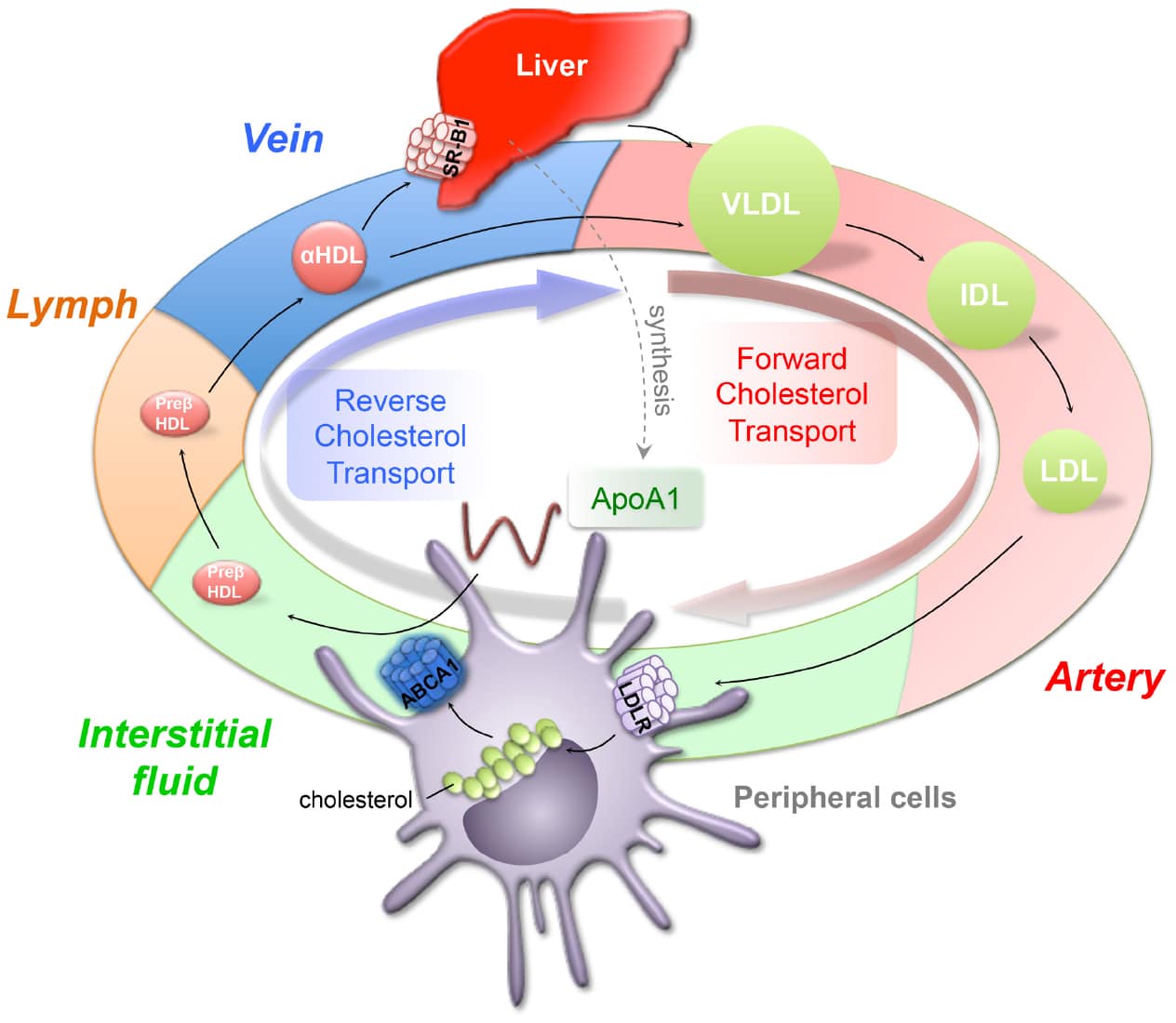
Lymphatic dependent reverse cholesterol transport within the peripheral tissues. HDL particles cross the vascular endothelium from plasma into interstitial fluid. Lipid-poor ApoA1 facilitates cellular cholesterol efflux through ABCA1-mediated pathway to form pre-HDL. Lymphatic capillaries have discontinuous button-like junctions, which are permeable for optimal fluid uptake. Lymphatic flow is driven by the pumping action of downstream collecting lymphatic vessels . Ultimately, lymph ends up in the thoracic duct that crosses the lymphovenous valve and drains into the subclavian vein.
Also Check: What Happens When Your Cholesterol Level Is Too High
What Protein Transports Cholesterol
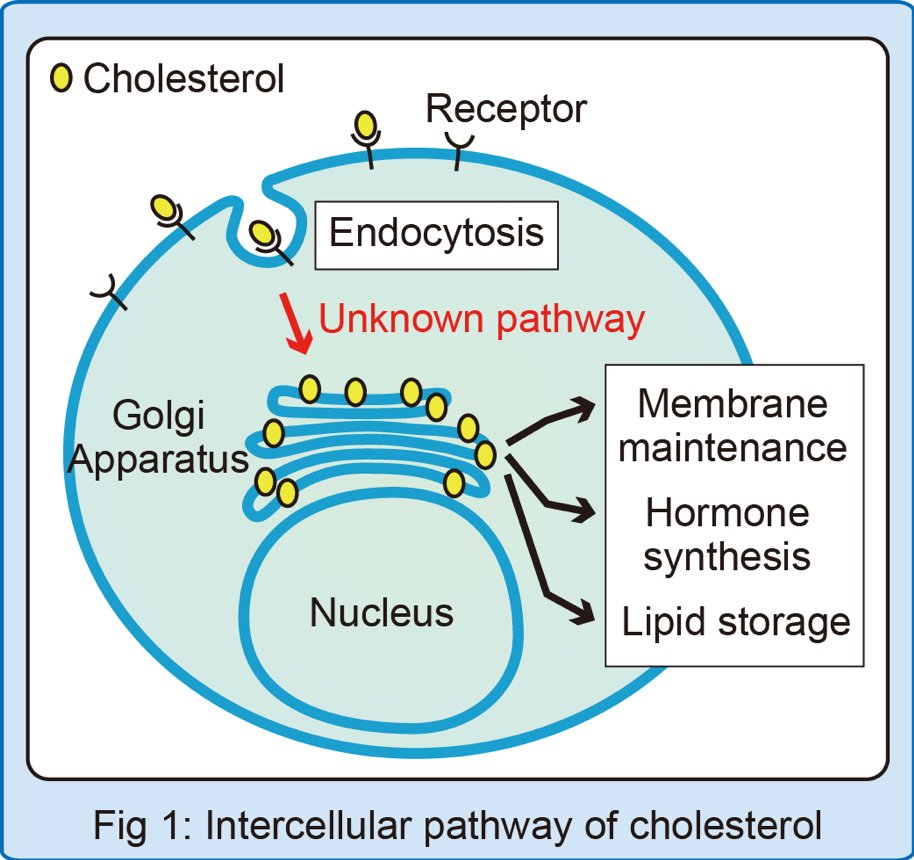
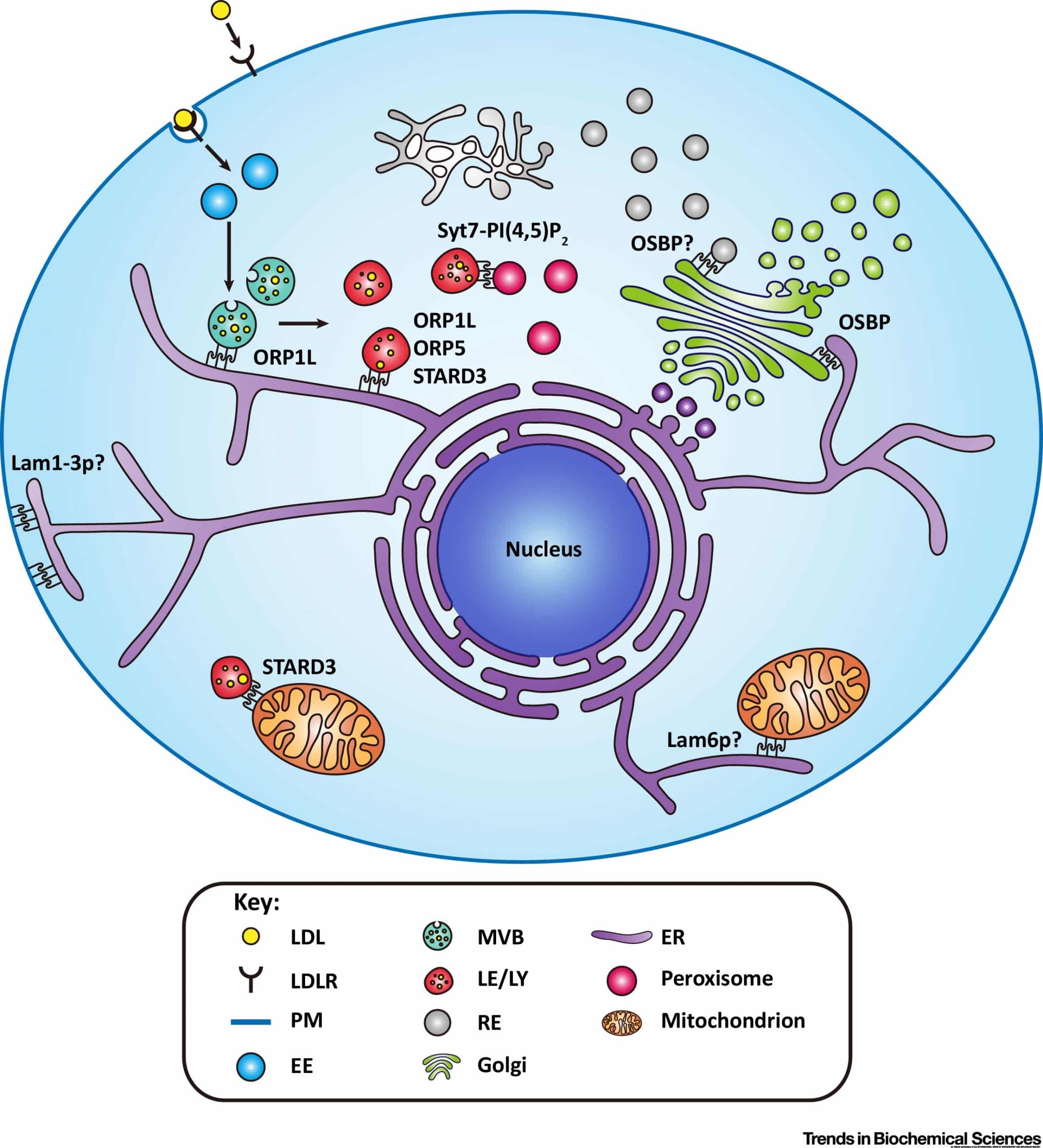
Cholesterol is dynamically transported among membrane-bound organelles primarily by nonvesicular mechanisms. Sterol transfer proteins bind cholesterol in their hydrophobic pockets and facilitate its transfer across the aqueous cytosol.
Where does cholesterol travel in the human body?
Cholesterol travels through the blood on proteins called lipoproteins. Two types of lipoproteins carry cholesterol throughout the body:
Do You Need To Limit Dietary Cholesterol
For most people, the answer might not be what you expect. We dive into the science to explain why.
Cholesterol is arguably one of the most misunderstood nutrients. Remember the days when eating egg yolks was a diet taboo? Or when there was a low-fat version of everything? This is in large part due to misconception that many held around dietary cholesterol and how it influences your health.
Luckily for us, more and more research is coming to light about cholesterol levels, heart health, the cholesterol thats naturally present in food and how theyre all intertwined. In short, dietary cholesterol doesnt directly raise your blood cholesterol levels. And there are several foods we can eat that boost our good cholesterol levels and lower our bad cholesterol levels. So, you dont need to strictly limit your dietary cholesterol in that name of healthy cholesterol levels. Here we dive into the science to explain why.
Read Also: How Much Cholesterol Is There In Shrimp
Read Also: Does Trans Fat Cause High Cholesterol
A Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Ldlr Pathway
Familial hypercholesterolemia is one of the most common inborn errors of metabolism and the most common in the category of monogenic defects of cellular cholesterol processing . In most cases, it is an autosomal dominant disorder, with the heterozygous state affecting 1 in 500 individuals . There is a strong gene dosage effect, and the rare homozygous FH patients exhibit a very severe clinical phenotype. The majority are caused by mutations in the LDLR gene. A rarer, clinically indistinguishable phenotype is caused by mutations in apoB, the ligand for the LDLR. In the latter case, the disease is referred to as familial defective apoB-100.
A third locus underlying autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia, PCSK9 , was recently identified . In addition to an increasing number of patient mutations, there is suggestive evidence for the involvement of PCSK9 gene variants in affecting total and LDL cholesterol levels in the population . PCSK9 is a serine protease in the secretory pathway and plays an important role in controlling LDLR levels, but the precise mechanism remains to be resolved. In principle, increased LDL cholesterol in the absence of PCSK9 function could reflect decreased clearance or increased hepatic secretion of apoB-containing lipoproteins. Both possibilities are being investigated .
How Do Chylomicrons Transport Cholesterol
Chylomicrons predominately transport triacylglycerols to adipose tissue and muscle as fatty acids, but also deliver dietary cholesterol taken up by enterocytes in the lumen to the liver. Once most of the triacylglycerols have been delivered to the adipose tissue and muscle, the remnants of the lipoprotein,
You May Like: How Do You Get High Cholesterol
Other Functions Of Hdls
The preceding sections focused on the role of HDLs in cholesterol transport and the central role of apo A1 in regulating RCT. Recently other protective functions of HDLs against oxidation, infection, and inflammation have been documented . These functions are of course indirectly related to RCT because without the activities of apo A1, ABCA1, and LCAT there would be no HDLs in the circulation to support these functions. Nevertheless, factors promoting apo A1 recycling may be different from those that depend on HDL cholesterol levels. Large HDLs are the preferred scaffold for enzymes such as paraoxonases and platelet activating factor hydrolase that can degrade oxidized phospholipids that promote apoptosis. As part of the inflammatory response, these protective enzymes are displaced from HDLs and significant changes occur in HDL lipid composition.
What Carries Cholesterol Away From Cells
HDL stands for high-density lipoproteins. It is sometimes called the good cholesterol because it carries cholesterol from other parts of your body back to your liver. Your liver then removes the cholesterol from your body. LDL stands for low-density lipoproteins.
Where is cholesterol stored?
Though some cholesterol components are stored in the liver and gallbladder, the main storage area for excess lipoproteins is in fat cells called adipocytes. When you have too much cholesterol, these cells swell up and you gain weight.
Also Check: How To Calculate Ldl Cholesterol Formula
Where Is Cholesterol Made
Some cholesterol comes from the food we eat, but most is made in the liver in a complex 37-step process.
Cholesterol and another type of blood fat called triglycerides can’t circulate loosely in the blood, so the liver packages them into parcels called lipoproteins, including LDL and HDL cholesterol.
They are released into the blood to carry the fats around the body to wherever they’re needed.
Estimation Of Ldl Particles Via Cholesterol Content
Chemical measures of lipid concentration have long been the most-used clinical measurement, not because they have the best correlation with individual outcome, but because these lab methods are less expensive and more widely available.
The lipid profile does not measure LDL particles. It only estimates them using the Friedewald equationby subtracting the amount of cholesterol associated with other particles, such as HDL and VLDL, assuming a prolonged fasting state, etc.:
- L T
- where H is HDL cholesterol, L is LDL cholesterol, C is total cholesterol, T are triglycerides, and k is 0.20 if the quantities are measured in mg/dl and 0.45 if in mmol/l.
There are limitations to this method, most notably that samples must be obtained after a 12 to 14 h fast and that LDL-C cannot be calculated if plasma triglyceride is > 4.52 mmol/L . Even at triglyceride levels 2.5 to 4.5 mmol/L, this formula is considered inaccurate. If both total cholesterol and triglyceride levels are elevated then a modified formula, with quantities in mg/dl, may be used
- L T
This formula provides an approximation with fair accuracy for most people, assuming the blood was drawn after fasting for about 14 hours or longer, but does not reveal the actual LDL particle concentration because the percentage of fat molecules within the LDL particles which are cholesterol varies, as much as 8:1 variation.
Normal ranges
Don’t Miss: Is A Keto Diet Bad For Cholesterol
The Role Of The Lymphatic System In Cholesterol Transport
Minghan Wang, Janssen, USAAndrew L. Siebel, Baker IDI Heart and Diabetes Institute, Australia Suowen Xu, University of Rochester, USA Andrew J. Murphy, Baker IDI Heart and Diabetes Institute, Australia Donato Santovito, Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich, GermanyLi-Hao Huang and Gwendalyn J. Randolph, Department of Pathology and Immunology, Washington University School of Medicine, 425 South Euclid, St. Louis, MO 63110, USA, Copyright
Keeping These Numbers In Check
There are several things that influence your cholesterol numbers, some of which you have control over. While heredity and weight may play a role, lifestyle choices around diet and exercise can also raise or lower your overall numbers.
Eating foods that are low in cholesterol and saturated fats, getting regular exercise, and managing your weight are all
Read Also: Medicine For High Cholesterol And High Triglycerides
Lipid Transport Storage And Utilization
Once dietary lipids are digested in the gastrointestinal tract and absorbed from the small intestine, they need to be transported around the body so they can be utilized by cells or stored for later use. Once again, the fact that lipids arent water-soluble means that they need some help getting around the watery environment of the body. Lets take a look at how this works.
Lipid Transport From The Liver
The contents of chylomicron remnants, as well as other lipids in the liver, are incorporated into another type of lipoprotein called very-low-density lipoprotein . Similar to chylomicrons, the main job of VLDL is delivering triglycerides to the bodys cells, and lipoprotein lipase again helps to break down the triglycerides so that they can enter cells .
As triglycerides are removed from VLDL, they get smaller and more dense, because they now contain relatively more protein compared to triglycerides. They become intermediate-density lipoproteins and eventually low-density lipoproteins . The main job of LDL is to deliver cholesterol to the bodys cells. Cholesterol has many roles around the body, so this is an important job. However, too much LDL can increase a persons risk of cardiovascular disease, as well discuss below.
High-density lipoproteins are made in the liver and gastrointestinal tract. Theyre mostly made up of protein, so theyre very dense. Their job is to pick up cholesterol from the bodys cells and return it to the liver for disposal.
Figure 5.27. Overview of lipoprotein functions in the body.
You May Like: How Long To Fast Before Cholesterol Panel
Don’t Miss: What Is A Good Non Hdl Cholesterol Number
Understanding Blood Cholesterol Numbers
A persons blood cholesterol numbers can be one indicator of their risk of developing cardiovascular disease. This is a standard blood test, also called a lipid panel, that reports total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and triglycerides. When doctors assess a persons risk of cardiovascular disease, they consider these numbersalong with other risk factors like family history, smoking, diabetes, and high blood pressurein determining their recommendations for lifestyle changes or prescribing medications.
You might be familiar with LDL and HDL as good cholesterol and bad cholesterol, respectively. This is an oversimplification to help people interpret their blood lipid values, because cholesterol is cholesterol its not good or bad. The cholesterol in your food or synthesized in your body is all the same cholesterol molecule, and you cant consume good or bad cholesterol. In reality, LDL and HDL are both lipoproteins that carry cholesterol. A more appropriate descriptor for LDL might be the bad cholesterol transporter. We can think of HDL as the good cholesterol transporter, although the more researchers learn about HDL, the more they realize that this is also an oversimplification.
- coronary artery disease
- carotid artery disease
- peripheral artery disease
- chronic kidney disease
How To Improve Lipoprotein Levels
Various dietary and lifestyle modifications can impact lipoprotein levels and reduce the risk of disease.
If blood tests show that lipid levels are not within appropriate limits, a doctor will likely discuss the options for managing them.
Current recommendations for optimal blood lipid levels for adults aged 20 years and over are as follows:
- triglycerides: under 150 milligrams per deciliter
- LDL cholesterol: under 100 mg/dl
- HDL cholesterol: at least 40 mg/dl for males and 50 mg/dl for females
- total cholesterol: 125200 mg/dl
- non-HDL: less than 130 mg/dl
Below are some evidence-based ways to reach and maintain these optimal levels.
- Eating more fiber: A high-fiber diet can reduce LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels by 510%. Examples include beans, fruits, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
- Reducing excess body fat: This can HDL levels, decrease LDL and triglyceride levels, and help cut heart disease risk.
- Increasing physical activity: Exercise can help lower blood lipid levels, boost HDL levels, and may the concentration of small, dense LDL particles.
- Limiting added sugar and processed foods: Studies have unhealthy lipoprotein levels and high triglyceride levels.
- Cutting out processed meats: Studies have with unhealthy blood lipid levels.
- Choosing healthy fats: Fats from avocados, olive oil, nuts, and seeds improve blood lipid levels and decrease heart disease risk.
- Taking an omega-3 supplement:
Recommended Reading: Prescription Omega 3 For Triglycerides
Does Cholesterol Really Cause Atherosclerosis
Put simply: pretty much, yes. If you go to the doctor, and get your bad cholesterol measured, that will predict heart disease risk very well. But the details are a bit more complicated, so lets go over them.
Low density lipoproteins are one of several types of particles that transport fats in the blood. Fats need to be packaged like this since theyre hydrophobic , and the blood is mostly water.
The liver releases fats to the bloodstream by packaging them in very-low density lipoproteins that contain both triglycerides and cholesterol. These VLDLs provide the body with fats, and in the process of delivering those fats, are transformed into LDL.
LDL particles are very widely accepted as being a main cause of atherosclerosis. But clinics dont usually measure LDL particles. Insead, they usually measure the amount of cholesterol contained in LDL particles: LDL-C. Because LDL is very cholesterol-rich, this serves as an excellent proxy for LDL levels in the blood, and thus correlates very well to atherosclerotic risk.
But the blood level of LDL-C alone does not tell the whole story of atherosclerosis.
Second, preliminary evidence suggests that LDL particles with different densities have differing atherosclerotic potential: small dense LDL particle levels better predict heart disease risk and may be able to cause more damage than large buoyant LDL particles.
How Can I Raise My Hdl Level
If your HDL level is too low, lifestyle changes may help. These changes may also help prevent other diseases, and make you feel better overall:
- Eat a healthy diet. To raise your HDL level, you need to eat good fats instead of bad fats. This means limiting saturated fats, which include full-fat milk and cheese, high-fat meats like sausage and bacon, and foods made with butter, lard, and shortening. You should also avoid trans fats, which may be in some margarines, fried foods, and processed foods like baked goods. Instead, eat unsaturated fats, which are found in avocado, vegetable oils like olive oil, and nuts. Limit carbohydrates, especially sugar. Also try to eat more foods naturally high in fiber, such as oatmeal and beans.
- Stay at a healthy weight. You can boost your HDL level by losing weight, especially if you have lots of fat around your waist.
- Exercise. Getting regular exercise can raise your HDL level, as well as lower your LDL. You should try to do 30 minutes of moderate to vigorous aerobic exercise on most, if not all, days.
- Avoid cigarettes.Smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke can lower your HDL level. If you are a smoker, ask your health care provider for help in finding the best way for you to quit. You should also try to avoid secondhand smoke.
- Limit alcohol. Moderate alcohol may lower your HDL level, although more studies are needed to confirm that. What we do know is that too much alcohol can make you gain weight, and that lowers your HDL level.
Read Also: Low Cholesterol With High Triglycerides
Class B Scavenger Receptor B1
SR-B1 is expressed in the liver, adrenal glands, ovaries, testes, macrophages, and other cells. In the liver and steroid producing cells, it mediates the selective uptake of cholesterol esters from HDL particles. In macrophages and other cells, it facilitates the efflux of cholesterol from the cell to HDL particles.
How Does Cholesterol Work
Fat and cholesterol dont mix well with water. Since the human body is mostly made up of water, these two molecule types need to be packaged inside lipoproteins to travel through the bloodstream. These lipoproteins act as emulsifiers, allowing fats and cholesterol to circulate. Once the bodys cell receptors recognize the lipoproteins, fat and cholesterol are directed into specific tissues to perform certain functions.
Recommended Reading: What Does High Non Hdl Cholesterol Mean
What Causes High Cholesterol
To better understand how to maintain heart-healthy cholesterol levels, lets first look at what causes bad cholesterol. A variety of factors can cause high LDL levels . In many cases, it has nothing to do with diet and everything to do with genetics.
Familial hypercholesteremia, for example, is a defect on chromosome 19 that makes it difficult for the body to remove LDL from the blood. About 1 in 250 people have this condition, which puts them at risk for heart attacks and strokes at an early age.
When genetic conditions are not a factor, diet, exercise, smoking and drinking alcohol can certainly be. Obesity and poor lifestyle choices can lead to liver disease, diabetes, high blood pressure thyroid disease and kidney and adrenal gland issues, which can increase your cholesterol levels, putting your heart at risk.