What Kind Of Test Measures Cholesterol
Everyone over the age of 20 should get their cholesterol levels measured at least once every five years. Your healthcare provider will order a blood test that will indicate how much cholesterol is carried in your bloodstream. This test will give your cholesterol levels. Your provider might also order what is called a lipid panel or a lipid profile. The panel gives you the following numbers:
- Total cholesterol.
- Non-HDL cholesterol.
- Ratio between cholesterol and HDL.
There are advanced tests that break down the size and shapes of LDL cholesterol levels, and also give the LDL particle number, but those are not normally ordered. Some test makers say that the more advanced tests are better at indicating who is at risk for heart disease, but most providers still feel that the usual tests are adequate.
If Cholesterol Is Necessary Why Do We Have To Worry About How Much We Have
Having enough cholesterol to meet your needs is important. Having too much cholesterol can cause problems. If your cholesterol levels are high, the condition is called hypercholesterolemia. If your cholesterol levels are low, the condition is called hypocholesterolemia. It is not common to have cholesterol levels that are too low, but it can happen.
About Your Cholesterol Result
A cholesterol test can measure:
- total cholesterol the overall amount of cholesterol in your blood, including both good and bad cholesterol
- good cholesterol this makes you less likely to have heart problems or a stroke
- bad cholesterol this makes you more likely to have heart problems or a stroke
- triglycerides a fatty substance similar to bad cholesterol
When you get your result, you may just be told your total cholesterol.
You might be able to get separate results for your good and bad cholesterol and triglycerides. Ask your doctor or nurse.
Dont Miss: Are Baked Potatoes High In Cholesterol
Don’t Miss: Shrimp Cholesterol Myth
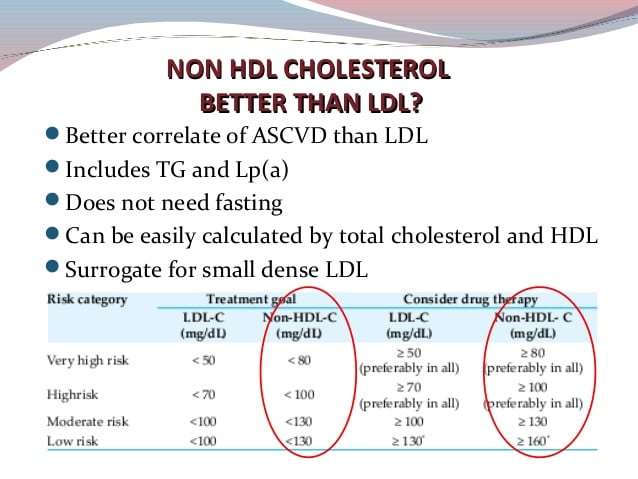
What Are Optimal Non
Our recommendations are based on recent research analyzing the non-HDL levels of more than 18,000 heart patients, as well as research on 202 heart patients who lowered their non-HDL levels over the course of one year, states Dr. James Kenney, Nutrition Research Specialist at the Pritikin Longevity Center.
Based on these data, our Pritikin Scientific Advisory Board recommends that non-HDL be no more than 100 for prevention and no more than 80 in those with established coronary artery disease or those at very high risk, such as people with diabetes or with evidence of severely clogged arteries, including those who have had a heart attack or have angina or claudication. Claudication is difficulty/pain in walking due to insufficient blood supply to the legs and feet.
And certainly, any significant improvement in non-HDL likely means significant reductions in heart attack risk.
Consistently, non-HDL levels improve, and rapidly so, among guests at the Pritikin Longevity Center. On average, they fall 24% within three weeks.
Research by scientists at UCLA has also found that two to three weeks at Pritikin leads to dramatic improvements in the quality of HDL particles, transforming them from pro-inflammatory to anti-inflammatory in nature.
Clinical Relevance Of Non

Anne L. Peters Clinical Relevance of Non-HDL Cholesterol in Patients With Diabetes. Clin Diabetes 1 January 2008 26 : 37.
IN BRIEF
Patients with type 2 diabetes have high rates of cardiovascular disease, much of which may be preventable with appropriate treatment of lipid abnormalities. Diabetic dyslipidemia most commonly manifests as elevated triglycerides and low levels of HDL cholesterol, with a predominance of small,dense LDL particles amid relatively normal LDL cholesterol levels. In diabetic patients, non-HDL cholesterol may be a stronger predictor of CVD than LDL cholesterol or triglycerides because it correlates highly with atherogenic lipoproteins. Target goals for LDL and non-HDL cholesterol in patients with diabetes are < 100 and < 130 mg/dl, respectively. Failure to consider the importance of non-HDL cholesterol in type 2 diabetes may result in undertreatment of patients with diabetes.
Table 1.
You May Like: Shrimp Has High Cholesterol
What Is An Optimal Non
For an optimal non-HDL cholesterol goal, one that gives us the best protection against heart attacks and other serious cardiovascular conditions, here is what recent evidence-based medicine tell us:
- The IMPROVE-IT1 trial, which followed 18,144 heart patients for 6 years, reported that non-HDL levels of 77 resulted in improved cardiovascular outcomes, including lower risk of heart attacks and cardiovascular deaths, compared to higher non-HDL levels.
- In the multicenter PRECISE-IVUS Trial2 treating 202 heart patients for 9 to 12 months, those who lowered non-HDL levels to 84 showed greater regression of coronary artery plaque than those with higher levels.
The Pritikin Scientific Advisory Board therefore recommends the following:
Also Check: Does Shrimp Raise Your Cholesterol
Why Is Ldl Cholesterol Still More Commonly Used Than Non
If non-HDL-C is a better indicator of cardiovascular risk than LDL-C and available with no additional cost or testing, the obvious question is: why is LDL-C still so commonly used instead?
That very question was addressed by the medical journalist, Larry Husten, in an article on MedPage Today.
In the article, Hudsen quotes an editorial from the New England Journal of Medicine, in which its author, Robert Heagele, writes that non-HDL-C is stable and reliable at very low levels and regardless of whether patients are tested while fasting. Furthermore, the non-HDL cholesterol level integrates all atherogenic lipoproteins, correlates well with apolipoprotein B, and predicts cardiovascular risk better than the LDL cholesterol level.
Although non-HDL-C and LDL-C often track closely, they diverge more prominently in people living with obesity, diabetes, and high triglycerides. For those people, non-HDL-C provides the greatest benefit over LDL-C.
However, it seems as though using LDL-C is so deeply ingrained in as common practice, that clinicians continue to do so even when the tools they use present non-HDL-C levels automatically.
The justification behind such an opinion, it seems, it that lipid values are but one of the markers used to determine cardiovascular risk. Other tests, such as electrocardiograms and blood tests, along with other risk factors such as blood pressure, smoking, and obesity, can all be used to determine ones cardiovascular risk profile.
Don’t Miss: How Much Cholesterol In Pork Chops
What Factors Affect Cholesterol Levels
A variety of factors can affect your cholesterol levels. They include:
- Diet: Saturated fat, trans fat and cholesterol in the food you eat increase cholesterol levels. Try to reduce the amount of saturated fat, trans fat and cholesterol in your diet. This will help lower your blood cholesterol level. Saturated and trans fat have the most impact on blood cholesterol.
- Weight: In addition to being a risk factor for heart disease, being overweight can also increase your triglycerides. Losing weight may help lower your triglyceride levels and raise your HDL.
- Exercise: Regular exercise can lower total cholesterol levels. Exercise has the most effect on lowering triglycerides and raising HDL. You should try to be physically active for 30 minutes on most days of the week.
- Age and sex: As we get older, cholesterol levels rise. Before menopause, women tend to have lower total cholesterol levels than men of the same age. After menopause, however, womens LDL levels tend to rise and HDL can drop.
- Heredity: Your genes partly determine how much cholesterol your body makes. High blood cholesterol can run in families.
What Are The Types Of Cholesterol
Cholesterol moves throughout the body carried by lipoproteins in the blood. These lipoproteins include:
- Low-density lipoprotein is one of the two main lipoproteins. LDL is often called the bad cholesterol.
- High-density lipoprotein is the other main lipoprotein. HDL is often called the good cholesterol.
- Very-low-density lipoproteins are particles in the blood that carry triglycerides.
Don’t Miss: Tuna Steak Cholesterol
How Can I Lower My Cholesterol
There are two main ways to lower your cholesterol:
- Heart-healthy lifestyle changes, which include:
- Heart-healthy eating. A heart-healthy eating plan limits the amount of saturated and trans fats that you eat. Examples include the Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes diet and the DASH Eating Plan.
- Weight Management. If you are overweight, losing weight can help lower your LDL cholesterol.
- Physical Activity. Everyone should get regular physical activity .
- Managing stress. Research has shown that chronic stress can sometimes raise your LDL cholesterol and lower your HDL cholesterol.
- Quitting smoking.Quitting smoking can raise your HDL cholesterol. Since HDL helps to remove LDL cholesterol from your arteries, having more HDL can help to lower your LDL cholesterol.
- Drug Treatment. If lifestyle changes alone do not lower your cholesterol enough, you may also need to take medicines. There are several types of cholesterol medicines available, including statins. The medicines work in different ways and can have different side effects. Talk to your health care provider about which one is right for you. While you are taking medicines to lower your cholesterol, you should continue with the lifestyle changes.
NIH: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
What Treatments Are Recommended For High Non
Comparable to other lipid disorders, the first steps in the treatment of elevated levels of non-HDL-C are to lose weight, reduce calories in your diet, and substitute polyunsaturated fats for saturated fats. If these steps do not have the desired effects , your healthcare practitioner may recommend that you start lipid-lowering therapy with statins.
Read Also: Cholesterol In Pork Chop
What Complications Are Possible If You Dont Treat High Cholesterol Levels In Your Blood
The main reason to treat high cholesterol is to prevent or treat coronary heart disease , also called coronary artery disease or CAD. CHD happens when heart is not able to get enough oxygen-rich blood to function well and kills more people in the U.S. than any other cause of death. CHD usually refers to the large arteries, but there is also a condition called coronary microvascular disease that affects the small vessels and causes damage.
Does High Cholesterol Mean You Have Clogged Arteries
Its clear that having high cholesterol can be harmful for your cardiovascular system because it can increase your risk of having clogged arteries . Arteries are the most common of your blood vessels where the plague buildups due to excessive cholesterol in the blood occur. Excessive amounts of cholesterol that travel through the blood can affect the blood flow inside the arteries which then eventually can make your heart work harder in pumping the blood. And if your blood flow cannot run as well as it should, there will be many serious complications that occur such as hypertension , heart disease, heart attack, and stroke.
What is the difference between HDL and LDL?
In general, cholesterol is classified by the type of particles that carry cholesterol in the blood called lipoprotein. So, lipoprotein itself is a package of protein-cholesterol. LDL and HDL are the most common kinds of cholesterol discussed when it comes to the issue of lowering the risk of heart disease.
While LDL stands for low density lipoprotein, HLD stands for high density lipoprotein. And as the name suggests, LDL is high in fatty deposits and cholesterol. On the other side, HDL is very low in cholesterol.
Overall, we can say that HDL is good cholesterol and LDL is bad cholesterol. How they work in affecting the blood flow inside arteries opposing each other. While high LDL increases the risk of creating more plague buildups on the arterys walls, HDL works in the opposite way !
Read Also: Does Shrimp Raise Cholesterol Levels
High Ldl Cholesterol Diagnosis
A blood test can check your LDL, HDL, and total cholesterol levels. It also measures triglycerides, a type of fat that stores extra energy from your diet. High triglyceride levels can make you more likely to have heart problems.
Experts recommend testing every 4 to 6 years. Youâll probably need it more often if you have heart disease or diabetes, or if high cholesterol runs in your family.
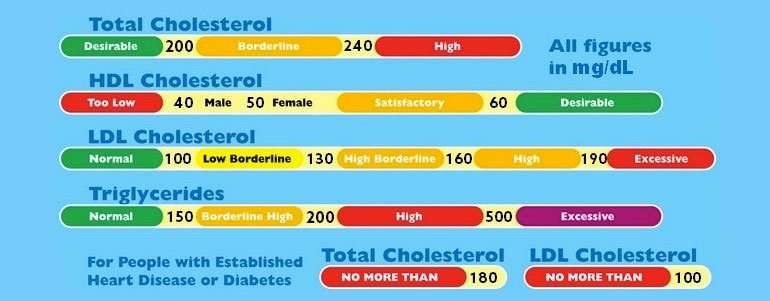
Lower numbers are better when it comes to LDL cholesterol test results. The general guidelines for adults in the United States are:
- Less than 100 milligrams per deciliter : Optimal
- 100-129 mg/dL: Near or above optimal
- 130-159 mg/dL: Borderline high
- 160-189 mg/dL: High
- 190 mg/dL and above: Very high
If you have a condition like heart disease or diabetes, your doctor might recommend an LDL target of 70 mg/dL or below.
How Often Should I Get A Cholesterol Test
When and how often you should get a cholesterol test depends on your age, risk factors, and family history. The general recommendations are:
For people who are age 19 or younger::
- The first test should be between ages 9 to 11
- Children should have the test again every 5 years
- Some children may have this test starting at age 2 if there is a family history of high blood cholesterol, heart attack, or stroke
For people who are age 20 or older::
- Younger adults should have the test every 5 years
- Men ages 45 to 65 and women ages 55 to 65 should have it every 1 to 2 years
Don’t Miss: What Is The Role Of Hdl
Why Is Cholesterol Important To Our Bodies
Every cell in the body needs cholesterol, which helps the cell membranes form the layers. These layers protect the contents of the cell by acting as the gatekeeper to what things can enter or leave the cell. It is made by the liver and is also used by the liver to make bile, which helps you digest foods. Cholesterol is also needed to make certain hormones and to produce vitamin D. Your liver makes enough cholesterol to meet your bodys needs for these important functions.
Better Predictor Than Ldl
In studies of patients with hypertriglyceridemia , it has been possible to establish a direct association between the values of non-HDL-C and the risk of death due to cardiovascular disease, this correlation being better than that observed when evaluating LDL-C.
In the case of male patients with high levels of Non-HDL-C, they have twice the risk of death from cardiovascular disease than their counterparts with low levels, while in female patients, the risk of death was approximately two and a half times higher. This is of major importance, since high values of LDL-C, have lower risk predictive power, especially in women.
Read Also: Seafood High In Cholesterol
Questions For Your Doctor About Test Results
To learn more about your non-HDL cholesterol test, you can raise one or more of the following questions with your doctor:
- What kinds of cholesterol were measured on my test?
- Which, if any, cholesterol levels were abnormal?
- What other factors do you consider when determining my cardiovascular disease risk?
- Do you recommend any follow-up testing?
- Based on my non-HDL cholesterol levels, should I make any lifestyle changes or begin any treatment to improve my cardiovascular health?
Results For People Aged 6079years
Results in people aged 6079years were moderately to strongly correlated with those aged 4059years . In virtually all countries, mean TC, non-HDL cholesterol and total-to-HDL cholesterol ratio declined more in these older age groups than in people aged 4059years. The decline advantage in older ages was particularly evident for Australia and the UK, where women and men aged 6079years experienced a decline in non-HDL cholesterol twice as large as those aged 4059years. The change in mean HDL cholesterol was larger in older ages in some countries and smaller in others, indicating that its change may be due to factors that are at least partly different from those affecting non-HDL cholesterol.
Change per decade in mean total cholesterol, non-HDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol and total-to-HDL cholesterol ratio in people aged 4059 vs 6079years. AUS, Australia BEL, Belgium CAN, Canada DEU, Germany ESP, Spain GBR, United Kingdom ITA, Italy JPN, Japan KOR, South Korea THA, Thailand USA, United States of America.
Read Also: Are Mussels High In Cholesterol
What Do Your Cholesterol Results Mean
When you have a cholesterol test, it is really important that your healthcare professional explains the results to you to prevent unnecessary worry and confusion.
Its not just your total cholesterol thats important and your results will include different types of cholesterol. If you are only given your total cholesterol, ask for a break-down of the other numbers. Its possible to have a healthy total cholesterol number but an unhealthy balance of the different types of cholesterol.
As a minimum, you should be given your total cholesterol and HDL numbers, then you can work out your ratio of total cholesterol to HDL cholesterol .
You might also have your triglycerides tested, these are another type of blood fat which are linked to heart disease.
Ask for a print out of your results if you are not able to speak to your GP, nurse or pharmacist.
Your results should include:
- Total cholesterol
This is sometimes written as ‘serum cholesterol’ or ‘TC’ and refers to your overall level of cholesterol.
- Non-HDL cholesterol
Your non-HDL cholesterol is your total cholesterol minus your HDL cholesterol. Its all the ‘bad’ cholesterol added together, including your LDL cholesterol. Ideally it should be as low as possible.
- HDL cholesterol
- TC:HDL ratio
You might be given a TC:HDL ratio, which is the ratio of HDL compared to the total cholesterol. If not, you can work it out from your HDL and total cholesterol numbers. This should be as low as possible. Above 6 is considered high.
When To See A Healthcare Provider
You most likely wont experience any symptoms of a low HDL level early on. Its important to meet with a healthcare provider consistently for routine bloodwork to monitor for silent risk factors for disease.
If your healthcare provider finds that you have abnormal cholesterol levels, they can help you get them into a healthy range. They may recommend medications, called statins, to help lower LDL levels.
Lifestyle changes to help to increase HDL levels include:
- Eat a healthy diet
- Sweating or a clammy feeling
- Loss of consciousness
Don’t Miss: Shellfish High In Cholesterol