The Biological Building Blocks
The cell is the basic unit of life. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. As will be discussed later, humans are made up of many millions of cells. In order to understand what goes wrong in cancer, it is important to understand how normal cells work. The first step is to discuss the structure and basic functions of cells.
First we will introduce the common building blocks of cells. All cells, regardless of their function or location in the body, share common features and processes. Amazingly, cells are comprised almost entirely of just four basic types of molecules. Shown above is a cell surrounded by examples of these building block molecules.
Since they are present in living things these building blocks are called biomolecules. The next sections describe the structures and functions of each of these basic building blocks. Further information on the topics on this page can also be found in most introductory Biology textbooks, we recommend Campbell Biology, 11th edition.1
Cyclic Forms Of Monosaccharides
As noted above, the preferred structural form of many monosaccharides may be that of a cyclic hemiacetal. Five and six-membered rings are favored over other ring sizes because of their low angle and eclipsing strain. Cyclic structures of this kind are termed furanose or pyranose , reflecting the ring size relationship to the common heterocyclic compounds furan and pyran shown on the right. Ribose, an important aldopentose, commonly adopts a furanose structure, as shown in the following illustration. By convention for the D-family, the five-membered furanose ring is drawn in an edgewise projection with the ring oxygen positioned away from the viewer. The anomeric carbon atom is placed on the right. The upper bond to this carbon is defined as beta, the lower bond then is alpha.Click on the following diagram to see a model of -D-ribofuranose.
Models of these glucose, galactose, mannose and allose pyranose structures may be viewed by .A practice page for examining the configurations of aldohexoses may be viewed by .
The ring size of these cyclic monosaccharides was determined by oxidation and chain cleavage of their tetra methyl ether derivatives. To see how this was done for glucose .
Testosterone Belongs To Which Class Of Macromolecules Nad Supplements Increase Testosterone
- Intermittent Fasting Increase Testosterone Can You Take Both Semanax And Male Enhancement Pills At The Same Time
- Best Testosterone Booster Supplement For Mood Swings
- Empower Testosterone Booster Plus How To Buy Duromax Male Enhancement
- What Do Testosterone Shots Do For Trans Men
- Vegetables To Increase Testosterone Levels
- How Can I Raise My Testosterone How Long Does It Take To Get Blood Test Results For Testosterone
- Low Testosterone What To Discuss With Doctor 30s How To Get Testosterone Tested
- How To Lose Water Weight From Testosterone
- Where Can I Buy Research Testosterone
- New Testosterone Booster Vitamin World Testosterone To Increase Sperm Count
Testosterone Supplements Prescription Does Weightlifting Increase Testosterone Production. Increase Testosterone Gout Increase Testosterone By Lifting Weights All Natural Men S Testosterone Booster. What Effects Do Testosterone Boosters Have Can Increasing Testosterone Increase Height Best Real Male Enhancement Pills.
Also Check: Is Wine High In Cholesterol
You May Like: How Much Cholesterol In Canned Tuna
What Are Hdl Ldl And Vldl
HDL, LDL, and VLDL are lipoproteins. They are a combination of fat and protein. The lipids need to be attached to the proteins so they can move through the blood. Different types of lipoproteins have different purposes:
- HDL stands for high-density lipoprotein. It is sometimes called “good” cholesterol because it carries cholesterol from other parts of your body back to your liver. Your liver then removes the cholesterol from your body.
- LDL stands for low-density lipoprotein. It is sometimes called “bad” cholesterol because a high LDL level leads to the buildup of plaque in your arteries.
- VLDL stands for very low-density lipoprotein. Some people also call VLDL a “bad” cholesterol because it too contributes to the buildup of plaque in your arteries. But VLDL and LDL are different VLDL mainly carries triglycerides and LDL mainly carries cholesterol.
How Macromolecules Come Together: Hydrolysis & Condensation Reactions
Biopolymers can be built from constituent monomers or broken down into constituent monomers through the process of anabolism or catabolism, respectively. Condensation reactions are the chemical process by which two molecules are joined with the loss of water, and is the process by which carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and proteins are synthesized from simpler subunits. Because water is lost, this process can also be called dehydration synthesis.
A-H + B-OH A-B + H2O
Hydrolysis reactions are those in which theaddition of water allows for essentially to the opposite process of condensation to occur, thereby cleaving a larger molecule into smaller substituent molecules.
A-B + H2O A-H + B-OH
Aoki-Kinoshita, K.F., An introduction to bioinformatics for glycomics research, PLoS Comput. Biol. 4, e1000075 .
Taylor, M.E. and Drickamer, K., Introduction to Glycobiology, Oxford University Press .
Spiro, R.G., Protein glycosylation: nature, distribution, enzymatic formation, and disease implications of glycopeptide bonds, Glycobiology 12, 43R56R .
Ninfa, A.J., Ballou, D.P., and Benore, M., Fundamental Laboratory Approaches for Biochemistry and Biotechnology , Wiley .
Tanford, C. and Reynolds, J., Natures Robots: A History of Proteins, Oxford University Press .
Bloomfield, V.A., Crothers, D.M., and Tinoco, I., Jr., Nucleic Acids. Structures, Properties, and Functions, University Science Books .
Recommended Reading: Does Tuna Have Good Or Bad Cholesterol
Also Check: Are Shrimp Bad For Cholesterol
Is Oil Better Than Lotion
The Benefits of Lotion Lotions moisturize dry skin: Nazarian opines that lotion has the edge over oil if were talking about moisturizing abilities. Because theyre partly water-based, theyre often better at penetrating the skin, and can deliver ingredients that improve the ability of the skin to maintain moisture.
The Big Fat World Of Lipids
ByEmily Carlson09 August 2012
When you have your cholesterol checked, the doctor typically provides your levels of three fats found in the blood: LDL, HDL and triglycerides. But did you know your body contains thousands of other types of fats, or lipids?
In human plasma alone, researchers have identified some 600 different types relevant to our health. Many lipids are also associated with diseases diabetes, stroke, cancer, arthritis, Alzheimer’s disease, to name a few. Learning more about them could point to new ways to diagnose and treat lipid-related conditions.
Lipid Encyclopedia
Just as genomics and proteomics spurred advances in the study of genes and proteins, lipidomics has offered a more quantitative and systematic approach to lipids research. Much of the effort has been led by a research consortium called LIPID MAPS. With funding from the National Institutes of Health, LIPID MAPS first major activity was classifying lipids into eight main categories. Six include fats from mammals and the other two include fats from bacteria, plants and marine life. Cholesterol belongs to the “sterol” group, and triglycerides are “glycerolipids.” Another category,”phospholipids,” includes the hundreds of lipids that constitute the cell membrane and allow cells to send and receive signals.
Lipid Mechanics
Using the lipidomics data and tools, members of LIPID MAPS have answered this last question.
Learn more:
Don’t Miss: Is Bone Marrow High In Cholesterol
What Can Raise My Risk Of High Cholesterol
A variety of things can raise your risk for high cholesterol:
- Age. Your cholesterol levels tend to rise as you get older. Even though it is less common, younger people, including children and teens, can also have high cholesterol.
- Heredity. High blood cholesterol can run in families.
- Weight. Being overweight or having obesity raises your cholesterol level.
- Race. Certain races may have an increased risk of high cholesterol. For example, African Americans typically have higher HDL and LDL cholesterol levels than whites.
What Is The Purpose Of A Glycosidic Bond
Glycosidic bonds are also the bonds that link the glucose units of glycogen, a primary form of energy storage in animal cells. They are the bonds that compose cellulose, which makes up the woody parts of plants and trees, and chitin, which provides the tough exoskeletons of beetles, crabs, and lobsters.
You May Like: Are Baked Potatoes High In Cholesterol
Lipid Sorting In Membrane Trafficking Processes
The role of other membrane components in determining the distribution of cholesterol among membranes raises the issue of how differences in these other membrane constituents are maintained. For proteins, the mechanisms of sorting based on molecular recognition are beginning to be understood in considerable detail. The same is not true for lipids. Maintenance of the distinct lipid compositions of organelles that are actively involved in membrane traffic suggests that there must be mechanisms for sorting lipids as transport vesicles and tubules are formed. This was proposed many years ago for the maintenance of the distinct lipid compositions of the apical and basolateral membranes of polarized epithelia . Similarly, the membrane constituents of GPI-anchored proteins confer the ability to be sorted selectively in the biosynthetic and endocytic pathways . In the endocytic pathway there is efficient sorting of fluorescent lipid analogs based on differences in their hydrocarbon chains .
Gnc Male Enhancement Best Natural Testosterone Supplement 2017
Will St John S Wort Increase Testosterone What Takes If You Inject Testosterone Into Fat Testosterone Belongs To Which Class Of Macromolecules. How To Read Low Testosterone Test Results Natural Ways To Increase Testosterone In Men. Male Enhancement Comparison Who Do You Say To Get Your Testosterone Levels Checked. Cannibis Testosterone Increase How Much American Ginseng To Boost Testosterone.
Do Testosterone Boosters Make You Hairy Natural Testosterone Booster Ncbi. Why Do Male Enhancement Pills Cause Nasal Congestion Do Testosterone Boosters Work For Older Men Step Up Male Enhancement Pills. How To Open Testosterone Vial Top Arnold Testosterone Booster.
Also Check: Is Bone Marrow High In Cholesterol
Recommended Reading: Does Shrimp Have High Cholesterol
What Are Lipid Rafts
Lipid rafts are possible areas of the cell membrane that contain high concentrations of cholesterol and glycosphingolipids. The existence of lipid rafts has not been conclusively established, though many researchers suspect such rafts do indeed exist and may play a role in membrane fluidity, cell-to-cell communication, and infection by viruses.
Lipid, any of a diverse group of organic compounds including fats, oils, hormones, and certain components of membranes that are grouped together because they do not interact appreciably with water. One type of lipid, the triglycerides, is sequestered as fat in adipose cells, which serve as the energy-storage depot for organisms and also provide thermal insulation. Some lipids such as steroid hormones serve as chemical messengers between cells, tissues, and organs, and others communicate signals between biochemical systems within a single cell. The membranes of cells and organelles are microscopically thin structures formed from two layers of phospholipid molecules. Membranes function to separate individual cells from their environments and to compartmentalize the cell interior into structures that carry out special functions. So important is this compartmentalizing function that membranes, and the lipids that form them, must have been essential to the origin of life itself.
What You Need To Know
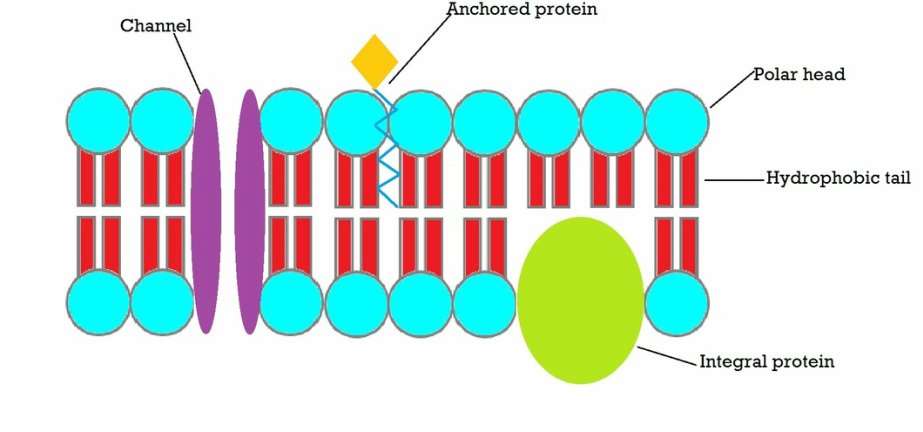
- You need to know the basic molecular structure and primary functions of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
- You need to know the role of enzymes as catalysts that lower the activation energy of biochemical reactions.
- You need to know how factors such as pH and temperature affect enzyme activity.
Also Check: How Do You Test Cholesterol
Which Macromolecule Is Wax
| Fats, phospholipids, waxes, oils, grease, steroids | |
| Proteins | Keratin , hormones, enzymes, antibodies |
| Nucleic acids |
Similarly, it is asked, what type of macromolecule is wax?
lipid
Additionally, what is an example of a macromolecule? Macromolecule ExamplesPolymers consist of subunits, called mers, that are covalently linked to form larger structures. Proteins, DNA, RNA, and plastics are all macromolecules. Many carbohydrates and lipids are macromolecules. Carbon nanotubes are an example of a macromolecule that is not a biological material.
Moreover, what biological macromolecule is wax similar to?
Lipids are a class of macromolecules that are nonpolar and hydrophobic in nature. Major types include fats and oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids.
What type of macromolecule is oil?
Molecular and Cell Biology For Dummies
| Group |
|---|
| Fats, oils, waxes, phosopholipids, steroids |
| *Lipids are not polymers. |
Anomeric Forms Of Glucose
Fischers brilliant elucidation of the configuration of glucose did not remove all uncertainty concerning its structure. Two different crystalline forms of glucose were reported in 1895. Each of these gave all the characteristic reactions of glucose, and when dissolved in water equilibrated to the same mixture. This equilibration takes place over a period of many minutes, and the change in optical activity that occurs is called mutarotation. These facts are summarized in the diagram below.
When glucose was converted to its pentamethyl ether , two different isomers were isolated, and neither exhibited the expected aldehyde reactions. Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of the pentamethyl ether derivatives, however, gave a tetramethyl derivative that was oxidized by Tollens reagent and reduced by sodium borohydride, as expected for an aldehyde. These reactions will be displayed above by clicking on the diagram.
Second, a pentamethyl ether derivative of the pyranose structure converts the hemiacetal function to an acetal. Acetals are stable to base, so this product should not react with Tollens reagent or be reduced by sodium borohydride. Acid hydrolysis of acetals regenerates the carbonyl and alcohol components, and in the case of the glucose derivative this will be a tetramethyl ether of the pyranose hemiacetal. This compound will, of course, undergo typical aldehyde reactions. By clicking on the diagram a second time this relationship will be displayed above.
Also Check: Is Canned Tuna Good For High Cholesterol
What Health Problems Can High Cholesterol Cause
If you have large deposits of plaque in your arteries, an area of plaque can rupture . This can cause a blood clot to form on the surface of the plaque. If the clot becomes large enough, it can mostly or completely block blood flow in a coronary artery.
If the flow of oxygen-rich blood to your heart muscle is reduced or blocked, it can cause angina or a heart attack.
Plaque also can build up in other arteries in your body, including the arteries that bring oxygen-rich blood to your brain and limbs. This can lead to problems such as carotid artery disease, stroke, and peripheral arterial disease.
Compare The Structures And Functions Of The Biomolecules Lipids And Starches
WARNING! This is a long answer
Explanation:
Starch consists of a large number of glucose units joined together.
There are two forms of starch.
Amylose is a linear chain of -D-glucose units joined by 14 linkages.
Plant amylopectin has a branched structure in which about one residue in every twenty is also has 16 linkages.
The body stores glucose as glycogen in muscle and liver. The structure of glycogen is like that of amylopectin, but the 16 branches occur about every 8 to 10 glucose units.
Starch and glycogen contain many OH groups. They are hydrophilic molecules.
Function
Starch is the main source of energy in plants.
Glycogen is the main source of energy in the body. Muscle glycogen is used in the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate during muscle contraction. Liver glycogen maintains the blood glucose concentration.
LIPIDS
Lipids have many different structures and functions. They are insoluble in water. Many have a polar “head” and a nonpolar “tail”. The most common types of animal lipids are fats, phospholipids, steroids.
FATS
Fats are esters of three fatty acids and glycerol .
Function
Fats store energy, help to insulate the body, and cushion and protect organs.
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
Structure
A phospholipid consists of two fatty acids, a glycerol unit, a phosphate group. and a polar molecule. The phosphate group and polar head region of the molecule are hydrophilic. The fatty acid tail is hydrophobic.
Function
Phospholipids are a major component of the cell membranes.
You May Like: Is Goat Cheese Bad For Cholesterol
Summary Of Recent Advances
Despite its importance for mammalian cell biology and human health, there are many basic aspects of cholesterol homeostasis that are not well understood. Even for the well-characterized delivery of cholesterol to cells via lipoproteins, a novel regulatory mechanism has been discovered recently, involving a serum protein called PCSK9, which profoundly affects lipoproteins and their receptors. Cells can export cholesterol by processes that require the activity of ABC transporters, but the molecular mechanisms for cholesterol transport remain unclear. Cholesterol levels in different organelles vary by 510 fold, and the mechanisms for maintaining these differences are now partially understood. Several proteins have been proposed to play a role in the inter-organelle movement of cholesterol, but many aspects of the mechanisms for regulating intracellular transport and distribution of cholesterol remain to be worked out. The endoplasmic reticulum is the main organelle responsible for regulation of cholesterol synthesis, and careful measurements have shown that the proteins responsible for sterol sensing respond over a very narrow range of cholesterol concentrations to provide very precise, switch-like control over cholesterol synthesis.
Why Is Cholesterol Important
Cholesterol is a very important steroid to the body. Its formed in the liver, brain tissue, bloodstream, and nerve tissue. Its a precursor to certain hormones, such as testosterone. This means the body needs cholesterol to create these hormones.
Cholesterol is also an important component of bile salts. These help break down dietary fats. Cholesterol is in all cell membranes. Cell membranes provide structure in your body and protect the inside of the cell.
Doctors classify cholesterol into low-density lipoprotein and high-density lipoprotein . Doctors commonly call HDL cholesterol the good kind of cholesterol, because it circulates in the blood and removes excess, unwanted cholesterol.
LDL cholesterol is the type that can lead to buildup in the bodys arteries. Over time, these deposits can harden. This narrows the flow of blood through the vessels. The result is a condition known as atherosclerosis. It can cause conditions like high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
A doctor can perform a blood test known as a lipid panel to determine if your blood cholesterol levels are too high or if you may be at risk for atherosclerosis. A doctor can review the results of your cholesterol test and compare it to people your age.
Cholesterol levels are measured in milligrams per deciliter of blood . Heres a breakdown of healthy cholesterol levels by age and sex:
| Age |
Read Also: Does Shrimp Give You High Cholesterol