Animal Models Of Rct And Cholesterol Efflux
In support of the human studies, a number of experiments using transgenic animals indicate that disruption of one or more steps in RCT and cholesterol efflux can result in accelerated atherosclerosis, whereas over-expression of pivotal proteins in RCT and cholesterol efflux, such as apoA-I, PLTP, LCAT, and SR-B1, exerts atheroprotective effects. For instance, increased accumulation of cholesterol in peripheral tissues is observed in animals with apoA-I or ABCA1 deficiency, while over-expression of those genes may reduce atherogenesis.
ABCA1, which facilitates cellular cholesterol efflux, has generated considerable interest as a potential anti-atherogenic agent. In transgenic mice that over-express ABCA1, increased ABCA1 raised plasma HDL levels, increased cholesterol efflux from macrophages, and reduced diet-induced atherosclerosis in different mouse models. For example, transgenic mice strongly expressing ABCA1 showed an anti-atherogenic lipid profile, with elevated levels of HDL-C and apoA-I, and significantly less aortic atherosclerosis. In a recent study, increased recruitment of ABCA1-deficient leukocytes was seen in the arterial wall of LDL-receptor deficient mice. This indicates that leukocyte ABCA1 plays a critical role in the protection against atherosclerosis, and that ABCA1 is a leukocyte factor that controls the recruitment of inflammatory cells.
Foods To Eat And Avoid
Cutting down on fatty foods may reduce the impact of a fatty liver or NAFLD. Eating plenty of fruits and vegetables, and foods such as bread and potatoes that release energy slowly can help.
A diet with plenty of protein is a way of obtaining adequate energy supplies without eating high-cholesterol foods. Eggs, nuts, chicken breast, and pulses are excellent sources of protein.
Eating regularly and snacking between meals can be a healthful way for a person to get enough fuel.
A person can help prevent health problems, such as damage to the liver, by reducing high levels of LDL cholesterol.
They can lower cholesterol by eating a healthful diet, with plenty of fruits and vegetables.
Saturated fats contain a high level of cholesterol.
Many fast foods, cakes, butter, fatty meats such as sausages, full-fat cheese, and cream contain saturated fats.
Taking regular exercise can help to lower a persons cholesterol. Giving up smoking can also be beneficial.
In Vitro Studies On Modification Of Rct And Cholesterol Efflux
There should be many factors that modify RCT and cholesterol efflux. For example, some pro-inflammatory factors can impair RCT and cholesterol efflux, whereas others may accelerate the pathway in cell culture models. Understanding and exploration of these factors may reveal underlying mechanisms of RCT and cholesterol efflux, and subsequently provide new therapeutic approaches.
Activated CD4+ T cells present in the atherosclerotic lesion can secrete interferon-gamma . The incubation of foam cells with IFN- results in the reduction of HDL3-mediated cholesterol efflux. This decrease is not observed in other macrophage-activating factors, such as colony-stimulating factor. These findings suggest that IFN- contributes to the progression of an atherosclerotic lesion by altering the pathway of intracellular cholesterol trafficking in macrophage foam cells. Reiss et al. suggest that anti-inflammatory adenosine A2A receptor can minimize atherosclerotic changes. They showed that a selective A2AR agonist, CGS-21680, inhibits foam cell formation in human macrophages stimulated with immune-complex and IFN-. This implies a possible novel approach to developing agents that prevent atherosclerosis.
Also Check: What Is The Role Of Hdl
Proteolytic Cleavage In The Golgi Releases Srebp
Once SREBP reaches the Golgi, it is ambushed and cleaved by two specific proteases . Cleavage releases the DNA-binding domain of the protein from the membrane. This fragment then moves across the cytosol and enters the nucleus, where it binds to SRE sequence elements that increase the expression of HMG-CoA reductase and also of various other enzymes from the cholesterol synthesis pathway .
Another protein that is upregulated by SREBP and SRE is the LDL receptor, a membrane protein that mediates endocytosis of low density lipoprotein . In cells that do not synthesize cholesterol themselves, SREBP upregulates transcription of the LDL receptor,
Like SREBP and SCAP, HMG-CoA reductase is anchored in the ER membrane. This does not seem necessary for the chemistry it performs. Instead, this location facilitates the negative feedback regulation imposed on it by cholesterol. Indeed, the enzyme contains a sterol-sensing domain that is homologous to the one found in SCAP .
11.4
How Do Lipids Travel To The Liver What Happens To Them In The Liver
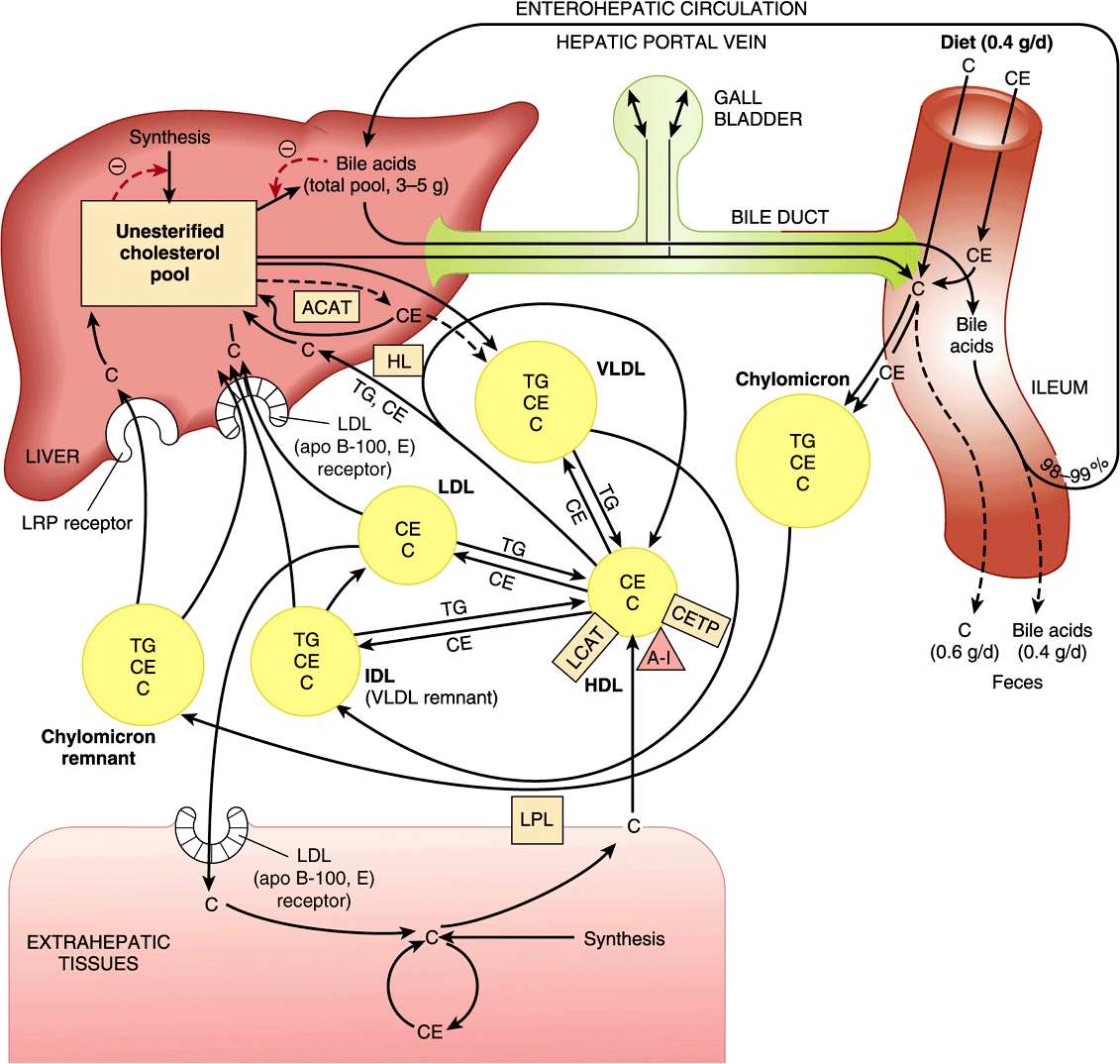
Dietary cholesterol is transported to the liver by chylomicron remnants which are formed from chylomicrons. High density lipoproteins take up cholesterol from tissues and other plasma lipoproteins. After the cholesterol is esterified, it is transferred ultimately to low density lipoproteins for uptake by the tissues.
Read Also: Seafood High In Cholesterol
Squalene Cyclization Yields The First Sterol Intermediate
The reactions shown here are catalyzed by squalene epoxidase and lanosterol synthase. The rearrangement indicated by the dashed arrow is not a real reactionââ¬âwe just rotate a couple of single bonds to show how the pieces fall into place for the subsequent cyclization.
The oxygen is introduced by squalene epoxidase, a cytochrome P450 enzyme. Such enzymes use NADPH to reduce one of the two atoms of molecular oxygen, while retaining the other one in a highly reactive state, which they then use toward their specific purposes . Squalene synthase inserts its active oxygen into a C=C double bond of the substrate to form an epoxide. The subsequent cleavage of the epoxide by lanosterol synthase starts a cascade of reactions that goes from one end of the molecule to the other, closing all four rings of the sterol skeleton in the process. Note that a methyl group also changes its place on the sterol ring the reaction mechanism is quite intricate.
11.2.6
Lipoproteins Transport Lipids Around The Body
Lipoproteins are transport vehicles for moving water-insoluble lipids around the body. There are different types of lipoproteins that do different jobs. However, all are made up of the same four basic components: cholesterol, triglycerides, phospholipids, and proteins.
The interior of a lipoproteincalled the lipid corecarries the triglycerides and cholesterol esters, both of which are insoluble in water. Cholesterol esters are cholesterol molecules with a fatty acid attached. The exterior of lipoproteinscalled the surface coatis made up of water-soluble components: proteins , phospholipids, and unesterified cholesterol. The phospholipids are oriented so that their water-soluble heads are pointed to the exterior, and their fat-soluble tails are pointed towards the interior of the lipoprotein.
While all lipoproteins have this same basic structure and contain the same four components, different types of lipoproteins vary in the relative amounts of the four components, in their overall size, and in their functions. These are summarized in the graph and table below, and the following sections give more details on the role of each type of lipoprotein.
|
Transports lipids from the small intestine, delivers TG to the bodys cells |
Transports lipids from the liver, delivers TG to bodys cells |
Formed as VLDL become depleted in TG either returned to liver or made into LDL |
Deliver cholesterol to cells |
Pick up cholesterol in the body and return to the liver for disposal |
Don’t Miss: Tuna Fish And Cholesterol
Understanding Blood Cholesterol Numbers
A persons blood cholesterol numbers can be one indicator of their risk of developing cardiovascular disease. This is a standard blood test, also called a lipid panel, that reports total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and triglycerides. When doctors assess a persons risk of cardiovascular disease, they consider these numbersalong with other risk factors like family history, smoking, diabetes, and high blood pressurein determining their recommendations for lifestyle changes or prescribing medications.
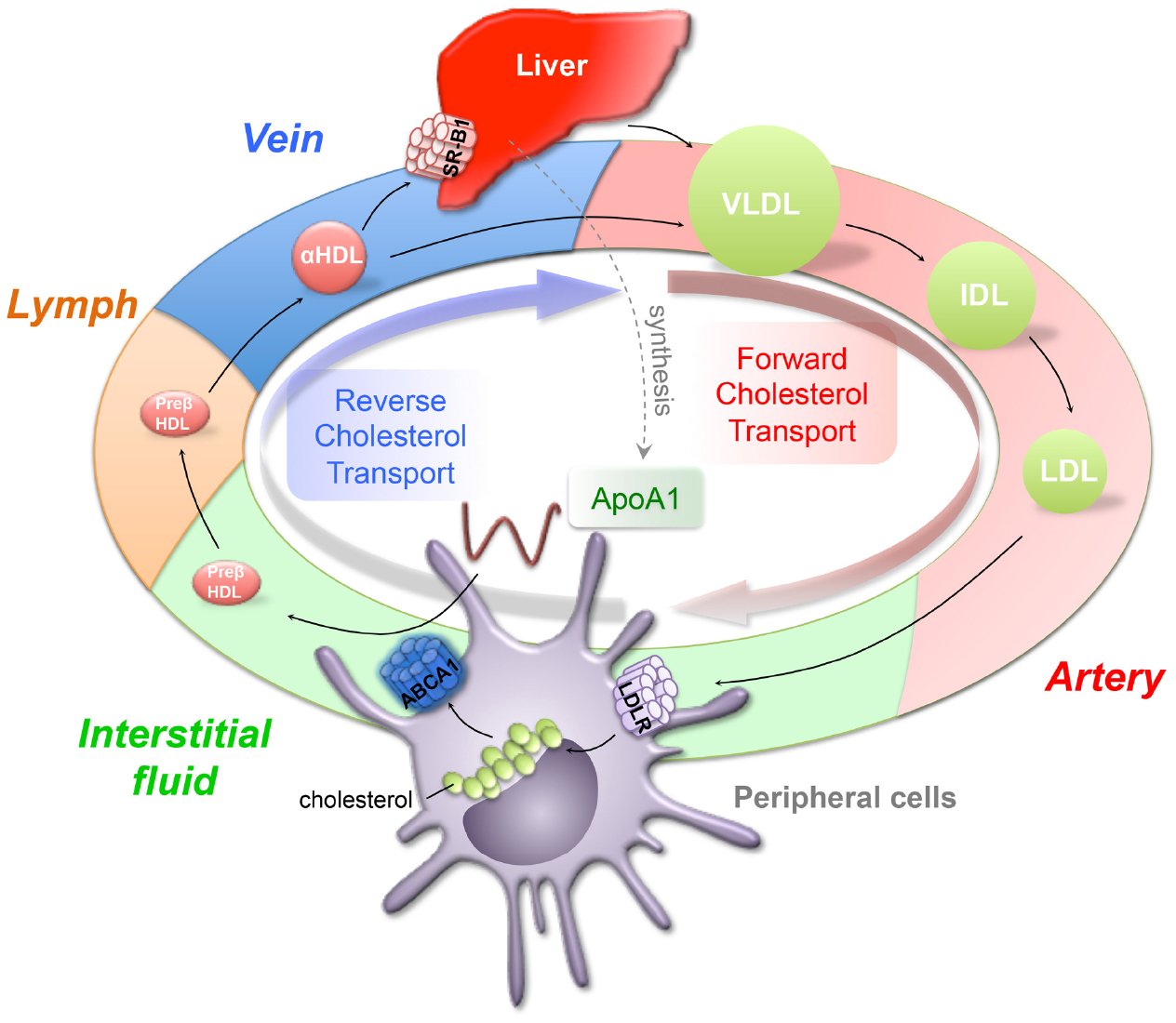
You might be familiar with LDL and HDL as good cholesterol and bad cholesterol, respectively. This is an oversimplification to help people interpret their blood lipid values, because cholesterol is cholesterol its not good or bad. The cholesterol in your food or synthesized in your body is all the same cholesterol molecule, and you cant consume good or bad cholesterol. In reality, LDL and HDL are both lipoproteins that carry cholesterol. A more appropriate descriptor for LDL might be the bad cholesterol transporter. We can think of HDL as the good cholesterol transporter, although the more researchers learn about HDL, the more they realize that this is also an oversimplification.
- coronary artery disease
- carotid artery disease
- peripheral artery disease
- chronic kidney disease
Hdl Levels And Atherosclerosis
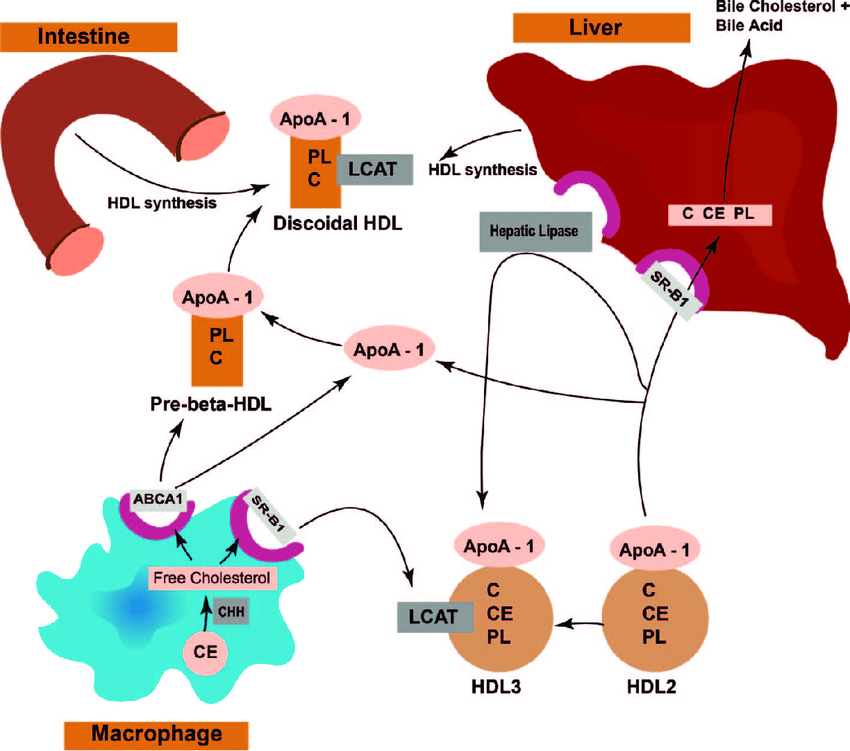
HDL has various species, identified on the basis of their major apolipoprotein components , density and electrophoretic mobility . Changes in HDL levels more closely reflect variations in the HDL2 subfraction rather than HDL3. Several studies have shown that low levels of HDL2 and HDL3 are associated with increased progression of atherosclerosis and risk of cardiovascular disease. Since HDL and ApoA-I are major receptors of cholesterol in the cholesterol efflux, increasing HDL levels may increase cholesterol efflux and RCT, contributing to reduced cardiovascular disease risks. Many attempts have been made to enhance HDL levels as anti-atherogenesis therapy.
Fibric acid derivatives are agonists of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor -, a nuclear hormone receptor involved in energy and lipid metabolism. Fibrates lower triglyceride levels very effectively, and raise HDL levels moderately. Fibrates are more effective in raising HDL levels when triglyceride levels are elevated. Gemfibrozil therapy significantly reduced cardiovascular disease, with a modest increase in HDL levels. A recent VA-HIT study demonstrated the benefit of gemfibrozil therapy in patients with low HDL and LDL levels.
Also Check: Cholesterol In Tuna
Lipoprotein Remodeling In Circulation
Cholesterol homeostasis is greatly modulated by proteins that catalyze the exchange of cholesterol and other lipids between circulating lipoprotein classes. Mutations in lipid transfer proteins are very important sources of lipoprotein phenotypic variation, as the genes are decidedly polymorphic. In plasma, there are two important lipid transfer proteins: cholesteryl ester transfer protein , and phospholipid transfer protein .
Which Is Lipoprotein Transports Cholesterol To The Liver
LDL Low-density lipoproteins transports cholesterol from the liver to cells. 80% of its total weight contain lipid. HDL High-density lipoproteins brings back cholesterol from the body tissues to the liver. 44% of its total weight contains lipid. Each lipoprotein has a varying proportion of triglycerides and cholesterol ester .
Recommended Reading: Cholesterol In Canned Tuna
Why Is Lipid Transport Important
5 Future directions. Cellular lipid transport is a fundamental process essential to all cell growth, division, and differentiation. Advances in reconstitution of lipid traffic in permeabilized cells and cell-free systems now allow for more precise and critical tests of protein function in transport processes.
Does Every Cell Produce Cholesterol
Cholesterol is an essential component of cell membranes. It is present in food and partially absorbed by the gut, but it is also synthesized by every cell in the body. However, only enterocytes and hepatocytes play a quantitatively important role in the synthesis of cholesterol that is present in plasma.
Also Check: Pork Chop Cholesterol
Hdl Versus Ldl Cholesterol
There are two main types of cholesterol: high-density lipoprotein and low-density lipoprotein . Lipoproteins are made of fat and proteins. Cholesterol moves through your body while inside lipoproteins.
HDL is known as good cholesterol because it transports cholesterol to your liver to be expelled from your body. HDL helps rid your body of excess cholesterol so its less likely to end up in your arteries.
LDL is called bad cholesterol because it takes cholesterol to your arteries, where it may collect in artery walls. Too much cholesterol in your arteries may lead to a buildup of plaque known as atherosclerosis. This can increase the risk of blood clots in your arteries. If a blood clot breaks away and blocks an artery in your heart or brain, you may have a stroke or heart attack.
Plaque buildup may also reduce blood flow and oxygen to major organs. Oxygen deprivation to your organs or arteries may lead to kidney disease or peripheral arterial disease, in addition to a heart attack or stroke.
Centers for Disease Control , over 31 percent of Americans have high LDL cholesterol. You may not even know it because high cholesterol doesnt cause noticeable symptoms.
The only way to find out if your cholesterol is high is through a blood test that measures cholesterol in milligrams per deciliter of blood . When you get your cholesterol numbers checked, youll receive results for:
To treat high cholesterol, doctors often recommend these lifestyle changes:
Structure And Function Of Cetp
CETP acts as a medium between lipoproteins for elevating plasma LDL-C level and lowering HDL-C level . A series of CETP inhibitors have been investigated in clinical, such as torcetrapib, dalcetrapib, evacetrapib, and anacetrapib . However, current inhibitors represent the turbulent beginning of CETP inhibition and an increased mortality rate related to off-target effects and lack of efficacy . Accompanying adverse effects call for a deeper exploration of the mechanism for CETP-mediated lipid transfer.
Figure 5.
The crystal structure of CETP and three-dimensional density maps of CETP binging lipoproteins. Atom figure of CETP. Secondary structure of CETP. Ternary complexes of HDL-CETP-LDL in cryo-EM micrographs. ~ the CETP insert into HDL, VLDL, LDL respectively in cryo-EM micrographs. the tunnel model of CETP-mediated lipid transfer .
However, there are some discrepancies with the tunnel model mentioned above. Matthias et al. used the experiments which involve three monoclonal antibodies to demonstrate that the antibodies binding on both ends of CETP do not inhibit CETPs function of transshipment cholesterol esters, but the antibodies on the middle does . In their research they supposed that the formation of the ternary tunnel complexes is not a mechanistic prerequisite by CETP to perform its functions. Hence, the real mechanism of CETP-mediated lipid transfer still remains to be studied and verified.
Read Also: Does Shrimp Raise Cholesterol Levels
Induction Of Obesity Impairs Reverse Cholesterol Transport In Ob/ob Mice
-
* E-mail:
Affiliations Heart Health, South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute, Adelaide, South Australia, Australia, Department of Cell Biology and Cardiovascular Medicine, Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, Ohio, United States of America
-
Roles Investigation, Methodology
Affiliation Department of Cell Biology and Cardiovascular Medicine, Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, Ohio, United States of America
-
Affiliation Heart Health, South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute, Adelaide, South Australia, Australia
-
Contributed equally to this work with: Christina Bursill, Stephen J. Nicholls
Roles Writing review & editing
Affiliation Heart Health, South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute, Adelaide, South Australia, Australia
-
Contributed equally to this work with: Christina Bursill, Stephen J. Nicholls
Roles Funding acquisition, Supervision
Affiliations Heart Health, South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute, Adelaide, South Australia, Australia, Department of Cell Biology and Cardiovascular Medicine, Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, Ohio, United States of America
Chylomicrons Deliver Lipids To Cells For Utilization And Storage
On the previous page, we learned that chylomicrons are formed in the cells of the small intestine, absorbed into the lymph vessels, and then eventually delivered into the bloodstream. The job of chylomicrons is to deliver triglycerides to the cells of the body, where they can be used as an energy source or stored in adipose tissue for future use.
How do the triglycerides get from the chylomicrons into cells? An enzyme called lipoprotein lipase sits on the surface of cells that line the blood vessels. It breaks down triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol, which can then enter nearby cells. If those cells need energy right away, theyll oxidize the fatty acids to generate ATP. If they dont need energy right away, theyll reassemble the fatty acids and glycerol into triglycerides and store them for later use.
As triglycerides are removed from the chylomicrons, they become smaller. These chylomicron remnants travel to the liver, where theyre disassembled.
Recommended Reading: Does Shrimp Raise Cholesterol
Ldl Transports Cholesterol To Cells Hdl Transports Cholesterol To Liver
- LDL transports cholesterol to cells HDL transports cholesterol to liver
If you can’t read please download the document
Post on 22-Dec-2015
Embed Size
TRANSCRIPT
- LDL transports cholesterol to cells HDL transports cholesterol to liver
- Slide 2
- LDL + cholesterol can form thrombus = clot Hemorheologichemodynamic theory: Slowed blood flow = mechanism for cholesterol buildup on arterial walls
- Slide 3
- Slide 4
- Acute Myocardial Infarction Delivery of oxygen by the coronary arteries LESS THAN Oxygen demand of the myocardial cell ~ 200-250 ml/min Excercising 200 ml/min Rest Exercise 1000 ml/min ~ 1000 ml/min NORMAL Myocardium uses > 75% of oxygen delivered to it!!!!!!!
- Slide 5
- Acute Myocardial Infarction Delivery of oxygen by the coronary arteries LESS THAN Oxygen demand of the myocardial cell ~ 200-250 ml/min Blockage of coronary = reduced flow.but there is no margin for reduced flow Excercising 200 ml/min Rest Exercise 1000 ml/min ~ 1000 ml/min NORMAL Clots & Narrowing Reduce Flow
- Slide 6
- Ischemic Cycling
Exogenous Lipid Metabolism In The Intestine
The amount of cholesterol absorbed from the diet is a major contributor to levels of cholesterol in circulation. One study has estimated that the complete abolition of dietary cholesterol absorption would reduce plasma cholesterol by up to 62% . About 50% of dietary cholesterol is absorbed through intestinal enterocytes, while the rest is excreted through feces . This figure however, is extremely variable among individuals and this variation has been established as an inherited trait . Thus, the mechanisms behind the entry of dietary cholesterol into the body are critical sources of variation in cholesterol homeostasis.
Recommended Reading: Tuna High In Cholesterol
Class B Scavenger Receptor B1
SR-B1 is expressed in the liver, adrenal glands, ovaries, testes, macrophages, and other cells. In the liver and steroid producing cells, it mediates the selective uptake of cholesterol esters from HDL particles. In macrophages and other cells, it facilitates the efflux of cholesterol from the cell to HDL particles.
Transcriptional Regulation Of Cholesterol Synthesis Starts In The Endoplasmic Reticulum
The sterol response element is a DNA consensus sequence that controls the transcription of HMG-CoA reductase. The corresponding SRE-binding protein is initially embedded in the ER membrane, and thus evidently unable to get in touch with its DNA target. SREBP is bound to a second protein, namely, SREBP cleavage activating protein . This protein is the actual cholesterol sensor it can adopt two different conformations, depending on the content of cholesterol in the surrounding membrane. The conformation that predominates at high cholesterol content lets SCAP bind to a third protein, INSIG.69 When this ternary complex forms, it is rapidly targeted toward proteolytic degradation, and that is the end of it.
At low cholesterol concentrations, however, SCAP does not bind to INSIG, and this is when things get interesting, as shown in the next slide.
11.3.2
Read Also: Cholesterol Hydrophilic Or Hydrophobic