Antibodies And Other Reagents
Mouse anti-ErbB2 , anti-ErbB2 , anti-Vinculin antibodies were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology . Rabbit anti-PARP antibody was purchased from Proteintech . Rabbit anti-phospho-Akt antibody was purchased from Cell Signaling Technology. Secondary goat anti-mouse and anti-rabbit, donkey anti-goat antibodies were obtained from LICOR. Neratinib and lapatinib were purchased from Selleck. Oleic acid and lovastatin were obtained from MeilunBio . Filipin was obtained from Sigma.
Gramd1s Play A Role In Accessible Cholesterol Transport From The Pm To The Er During Acute Expansion Of The Accessible Pool Of Pm Cholesterol
Acute expansion of the accessible pool of PM cholesterol results in the suppression of SREBP-2 cleavage and the inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis as a result of transport of accessible cholesterol from the PM to the ER. However, the intracellular transport machinery by which accessible cholesterol is transported from the PM to the ER remains unknown. GRAMD1s may play a role in this process, as they are able to sense and counteract the acute expansion of the accessible pool of PM cholesterol.
GRAMD1s-mediated PM to ER cholesterol transport plays a role in the suppression of SREBP-2 cleavage upon sphingomyelinase treatment.
-
Figure 6âsource data 1
Comparison of the recruitment to the PM of a wild-type GRAMD1b and of a mutant version of GRAMD1b that is defective in complex formation upon sphingomyelinase treatment.
HeLa cells expressing EGFPâGRAMD1b or EGFPâGRAMD1b TM swap were imaged under TIRF microscopy. Images were taken every 20 s, and 100 mU/ml of sphingomyelinase was added at the 10 min time point. Image size, 66.1 µm x 66.1 µm.
How Does Cholesterol Affect The Membrane
Due to the very small size of the polar headgroup compared to the cross-sectional area of the apolar portion, cholesterol is known to generate intrinsic negative curvature in lipid bilayers. Cholesterol thereby has the potential of promoting highly curved membrane structures such as lipid stalks that are proposed as lipid intermediates in membrane fusion.
Lipid bilayers exhibit resistance towards bending into curved structures that are different from their equilibrium structure. This is expressed in the curvature elasticity and is dependent upon the lipid composition.
Cholesterol increases the bending modulus and therefore the stiffness of fluid membranes, especially when they consist of saturated lipids and are in a state of Lo phase.
Cholesterol modulates the structure and activity of integral membrane proteins through different mechanisms. Cholesterol influences the behavior of membrane proteins in lipid bilayers in several ways. Generally, we distinguish between
global effects of the perturbed lipid bilayer, on membrane protein behavior and
specific effects of cholesterol binding to define binding motifs on membrane proteins.
The increased order of the lipid acyl chains leads to a reduction of free volume in bilayers when cholesterol is introduced. This increased free volume changes the conformational behavior and shifts the conformational equilibria of membrane proteins in the presence of cholesterol.
Read Also: Is Tuna Fish High In Cholesterol
What Are The Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane, also called the cell membrane, is the membrane found in all cells that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The plasma membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell.
What Does Cholesterol Do In The Cell Membrane Conclusion
After reading this article, it should be clear that cholesterol is a vital substance in any animals cells.
Firstly, it is essential to completing many bodily functions, secondly, it also plays a huge role in various metabolic pathways, and thirdly, it is fundamental for the functionality of the cell membrane.
The role of cholesterol in the cell membrane is vital. Cholesterol has the capacity to affect membrane fluidity not only by increasing the temperature range in which the cell membrane can continue to function, but it also serves as a barrier, as due to its chemical structure it can fit in spaces between phospholipids, preventing water-soluble substances from diffusing across the membrane.
Read Also: How Much Cholesterol In Crab
Effect Of Cholesterol On Membrane Fusion In Enveloped Virus Entry
Membrane fusion is a key step of enveloped virus entry into host cells . While viral surface glycoproteins drive membrane fusion, lipids including cholesterol play critical roles in the fusion process . A growing body of evidence supports the idea that cholesterol-rich regions serve as platforms for the entry of many enveloped viruses . The cholesterol requirement in virus entry has been evaluated by the inhibition of infection after cholesterol depletion from virus and/or host membranes by methylâcyclodextrin . Some viruses like the human immunodeficiency virus require cholesterol on both viral and target membranes for infection whereas others including the influenza virus require cholesterol only in the viral membrane . In either case, cholesterol depletion significantly impairs viral entry, but has little effect on viral binding to host cells, indicating that cholesterol is crucial for membrane fusion.
Cholesterol Plays A Role In Digestion
Cholesterol plays a role in digestion, due to the fact that it is an essential ingredient in the production of bile.
Bile is a substance that is produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder. It is responsible for the breakdown and absorption of some nutrients into the body.
Bile is an essential substance to have in the body, especially for the breakdown and digestion of dietary fats.
Cholesterol affects other essential parts of your health. While its good to know that cholesterol does in fact have positive benefits on the body, but it also shows the importance of regularly checking your cholesterol levels. When was the last time you checked your cholesterol levels?
Don’t Miss: Does Shrimp Have Bad Cholesterol
Cholesterol And Other Sterols
Cholesterol is an essential component of mammalian membranes and is a precursor for all steroid hormones. However, cholesterol can accumulate in certain tissues and cause serious pathological consequences in the body, such as artherosclerosis. Recently, the analysis of oxidation products of cholesterol has gained interest due to their putative pathophysiological role . There is also growing interest toward various plant sterols as their intake significantly reduces plasma cholesterol levels .
Sterols cannot be analyzed by ESIMS without derivatization as they are not readily ionized . Sandhoff et al. have used chemical sulfatation to achieve high-sensitivity detection of cholesterol . Cholesterol has also been derivatized with dimethylglycine, MDMABS , or ferrocenecarbamate . Notably, derivatization can be avoided by using APCI or APPI, which have been applied for the analysis of cholesterol and other sterols or oxidized cholesterol .
Mona H. Haron, … Asok K. Dasmahapatra, in, 2012
Normal Structure Of Cell Membranes
The normal structure of cell membrane is quite elastic, not rigid, and stretchable. High density cholesterol has been found to be more in normal cell membranes. The high density cholesterol accord the cell membrane with features suitable for carrying out its functions. High density cholesterol is the short tailed hydrocarbon. The kinks of the short tailed hydrocarbons are filled by sterols that further build up the structure of cell membranes and bi layers. The low density cholesterol is saturated hydro carbon with long tails and low combining capacity. These are not so efficient in giving the cell membrane the desired form.
Don’t Miss: Oysters High Cholesterol
Regulation Of Cholesterol Homeostasis
In humans, only about a third of the body cholesterol is of dietary origin , the remainder is produced by synthesis de novo in the endoplasmic reticulum.The latter must be tightly regulated as it is an energetically expensive process that requires appreciable amounts of acetyl-CoA, ATP, oxygen and the reducing factors NADPH and NADH, especially since cholesterol cannot be catabolized for energy purposes . The cholesterol in plasma membranes is associated with bilayer phospholipids, and any in excess of the binding capacity of the phospholipids circulates among the cell membranes through contact sites linking the organelles. In this way, phospholipids are believed to set a threshold level for cholesterol, and that in excess provides the feedback signal to multiple control mechanisms.
However, many other factors are involved in maintaining the large differences in cholesterol concentrations among the various membranes and organelles in cells within precise limits. These include regulatory proteins, and mechanisms that can involve either vesicle formation or non-vesicular pathways that utilize specific transport proteins, such as the ABC transporters.
Setting Your Browser To Accept Cookies
There are many reasons why a cookie could not be set correctly. Below are the most common reasons:
- You have cookies disabled in your browser. You need to reset your browser to accept cookies or to ask you if you want to accept cookies.
- Your browser asks you whether you want to accept cookies and you declined. To accept cookies from this site, use the Back button and accept the cookie.
- Your browser does not support cookies. Try a different browser if you suspect this.
- The date on your computer is in the past. If your computerâs clock shows a date before 1 Jan 1970, the browser will automatically forget the cookie. To fix this, set the correct time and date on your computer.
- You have installed an application that monitors or blocks cookies from being set. You must disable the application while logging in or check with your system administrator.
Also Check: Is Tuna Low In Cholesterol
Predict How A Cell Would Be Affected If The Cell Membrane Did Not Have Any Cholesterol Molecules
Who are the experts?Our certified Educators are real professors, teachers, and scholars who use their academic expertise to tackle your toughest questions. Educators go through a rigorous application process, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house editorial team.
Cholesterol plays an important part in the structure and function of the cell membranes of animals. Because animal cells do not have cell walls to support them, the cell membrane must maintain a strong but flexible surface. Cholesterol molecules inserted among the lipids that make up the membrane prevent the…
Is Cholesterol Good What Are Advantages Of Cholesterol Membrane Fluidity
The process of cell signaling would be hampered to a great extent, subsequently messing up the dependable cell functions. Cholesterol Membrane Fluidity is consequently essential for the everyday life process. The answer to how does cholesterol affect membrane fluidity relates to the potential benefits of cholesterol in humans.
Read Also: Which Of The Following Is Not A Function Of Cholesterol
You May Like: Does Shellfish Have High Cholesterol
Cholesterol And Actin Cytoskeleton Organization: Imaging Cells Using Confocal Microscopy
Altering the levels of cholesterol in cellular membranes will interfere with rafts organization. Decrease in membrane cholesterol content, for example, leads to rafts disruption and consequently alters, directly or indirectly, the cellular processes linked to these regions, such as signaling, membrane trafficking and cytoskeleton organization. Cytoskeleton organization, in particular, seems to play an important role in rafts cellular functions. It has long been shown that membrane rafts are not only enriched in signal transduction molecules, but also actin and actin binding proteins . Additionally, it was demonstrated that changes in cytoskeleton organization upon rafts disruption also alters signaling processes linked to this platform .
Fig. 3.
Representative image of actin filaments and the sites of binding of phalloidin. Fluorescence images of mouse embryonic fibroblasts treated or not with MCD 10 mM, fixed with 4% paraphormadehyde and labeled with phalloiding conjugated with Alexa fluor 546 . Arrows indicate the actin stress fibers in MCD treated cells.
A lot of other work corroborated these data showing that cholesterol depletion from cell plasma membrane leads to actin polymerization and reorganization. Most importantly, many of these works showed that changes in the actin cytoskeleton induced cell stiffness and changes in biomechanical properties of cells .
Also Check: How Much Cholesterol In Egg Beaters
What Is The Role Of Cholesterol In Eukaryotes
However, cholesterol plays an essential structural role in maintaining the fluidity of eukaryotic cell membranes. Since many receptors are localized to these cholesterol- and sphingomyelin-rich domains, it has been suggested that lipid rafts and caveolae function as signaling gateways into the cell.
Recommended Reading: Does Shrimp Increase Cholesterol
What Is The Function Of Cholesterol Molecules In The Plasma Membrane Of Human Erythrocytes
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â itâs anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â itâs anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
You May Like: Is Canned Tuna Bad For Cholesterol
Understanding The Role Of Cholesterol In Cellular Biomechanics And Regulation Of Vesicular Trafficking: The Power Of Imaging
Issue title: 200th Anniversary of Cholesterol
Article type: Research Article
Affiliations: Departamento de Morfologia, Bloco J3, sala 310, Instituto de Ciências Biológicas, UFMG, Av. Antonio Carlos, 6627, 31270-901, Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil. E-mail:
Keywords: Cholesterol, cell biomechanics, membrane trafficking, confocal microscopy, atomic force microscopy, laser tweezers, defocusing microscopy
DOI: 10.3233/BSI-160157
Journal: Biomedical Spectroscopy and Imaging, vol. 5, no. s1, pp. S101-S117, 2016
Abstract
You May Like: Is Tuna Fish Bad For Cholesterol
You May Like: Whole Wheat Pasta Cholesterol
Cell Culture And Transfection
HeLa and COS-7 cells were cultured in Dulbeccoâs modified Eagleâs medium containing 10% or 20% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin/streptomycin at 37ðC and 5% CO2. Transfection of plasmids was carried out with Lipofectamine 2000 . Both wild-type and genome-edited HeLa cell lines were routinely verified as free of mycoplasma contamination at least every two months, using MycoGuard Mycoplasma PCR Detection Kit . No cell lines used in this study were found in the database of commonly misidentified cell lines that is maintained by ICLAC and NCBI Biosample.
How Is Lipid Bilayer Formed
The formation of lipid bilayers is a self-assembly process. Water molecules are released from the hydrocarbon tails of membrane lipids as these tails become sequestered in the nonpolar interior of the bilayer. Furthermore, van der Waals attractive forces between the hydrocarbon tails favor close packing of the tails.
Don’t Miss: Is Chocolate Bad For Cholesterol
Are There Differences In Cell Membrane Cholesterol Levels Between Cell Types
With different cell types, and cell functions, are there distinct levels of cholesterol in each cell typeâs cell membrane, or do all cell types have a similar amount of cholesterol?
I am assuming certain cell types require different levels of cell membrane stability, and as such, different levels of cholesterol in that cell membrane.
Yes, there are differences in cell membraneâs cholesterol levels among different human cell types.
This table from Alberts shows the difference in cholesterol composition in a liver cell, a red blood cell and a Schwann cell/oligodendrocyte :
Table: Approximate Lipid Compositions of Different Cell Membranes
Besides that, the table shows that there is difference in the cholesterol composition among different membranes in the same cell . Actually, thatâs a more famous difference, depicted in this figure from Lehninger :
Figure: Lipid composition of the plasma membrane and organelle membranes of a rat hepatocyte. The functional specialization of each membrane type is reflected in its unique lipid composition. Cholesterol is prominent in plasma membranes but barely detectable in mitochondrial membranes.
The Plasma Membrane And Cellular Signaling
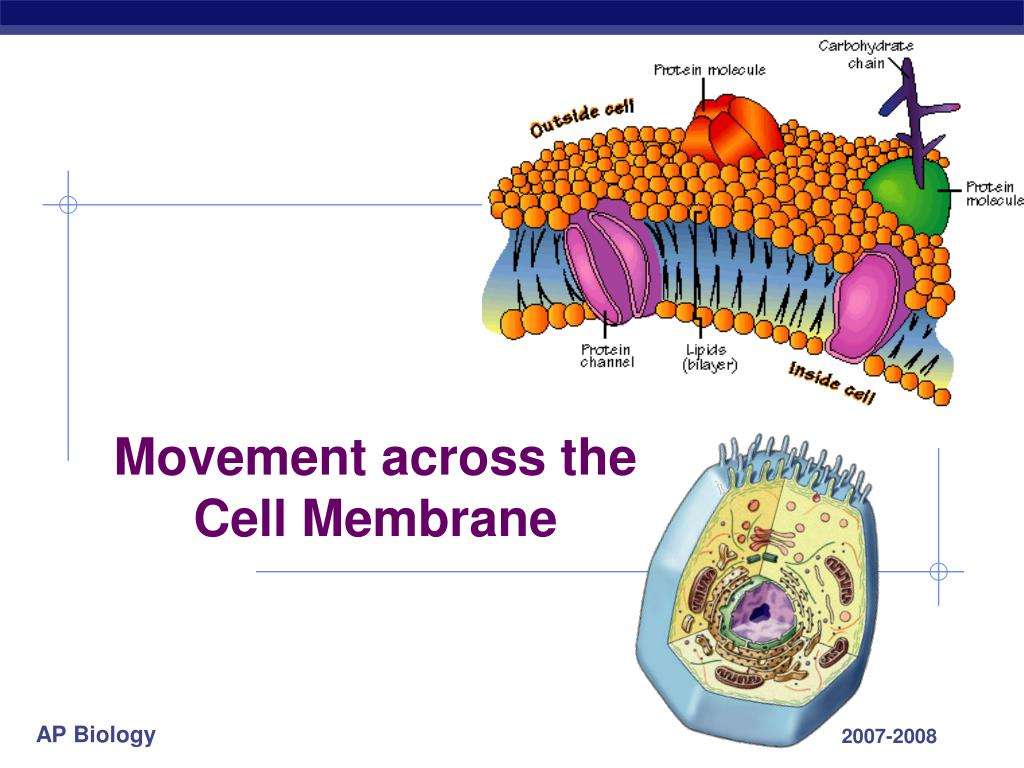
Among the most sophisticated functions of the plasma membrane is its ability to transmit signals via complex proteins. These proteins can be receptors, which work as receivers of extracellular inputs and as activators of intracellular processes, or markers, which allow cells to recognize each other.
Membrane receptors provide extracellular attachment sites for effectors like hormones and growth factors, which then trigger intracellular responses. Some viruses, such as Human Immunodeficiency Virus , can hijack these receptors to gain entry into the cells, causing infections.
Membrane markers allow cells to recognize one another, which is vital for cellular signaling processes that influence tissue and organ formation during early development. This marking function also plays a later role in the self-versus-non-self distinction of the immune response. Marker proteins on human red blood cells, for example, determine blood type .
Recommended Reading: Is Cholesterol A Hydrophobic Or Hydrophilic Molecule
Cholesterol Deficiency And Sonic Hedgehog Signaling
Cholesterol is an end product of the mevalonate pathway and is required for normal development. Ethanol has been shown to inhibit the mevalonate pathway and thus cholesterol biosynthesis . In mice, the lack of availability of cholesterol results in a drastic decline in sonic hedgehog signals transduction . Moreover, chicken and mouse embryos exposed to ethanol displayed reduced shh signaling . Therefore, alcohol-dependent inhibition of the cholesterol modification of shh produces morphologic defects which are similar to FASD phenotypes. In zebrafish embryos, ethanol treatment causes a dose-dependent reduction in cholesterol content, decreased cholesterol modification of shh, and a loss of shh signal transduction resulting in cyclopia, craniofacial hypoplasia, and holoprosencephaly . Further, supplementation of cholesterol is able to rescue the zebrafish embryos from these phenotypic defects.
N.S. Bhacca, in, 2000
Cholesterol Functions In The Cell Membrane
The cholesterol in the cell membrane achieve the following functions
- Structure of the cell and membrane
It is due to the presence of cholesterol molecules that cells get their structure. Cells with well-defined cell membranes exhibit distinct existence from surrounding cells. The presence of HDL in cell membranes accords them the required transmission capabilities to achieve balanced cell nutrition.
- Conduct of intercellular functions
An efficient cell membrane allows for the efficient conduct of intercellular processes with the cells. Within the cell, the cell organelles release chemicals and absorb molecules to synthesize and break down substances. A cell membrane of appropriate structure maintains boundaries and does not rupture untimely.
- Reverse transfer vehicles
HDL from cell membrane serves as vehicles for the reverse transfer of LDL to the liver where they get converted to bile. Thus HDL helps maintain the correct cholesterol balance and reduce excess LDL in the body.
Also Check: Are Oysters High In Cholesterol
Cholesterol Structure Dynamics And Membrane Topology
Cholesterol is a polycyclic amphipathic molecule derived from the sterane backbone . Its polar section is restricted to a single hydroxyl group which can form two distinct types of hydrogen bond with a polar group belonging to either a membrane lipid or a protein. The apolar section of cholesterol has an asymmetric structure with two distinct faces, referred to as and according to the system numeration of ring compounds proposed by Rose et al. . The face displays a planar surface, in contrast with the face which has a significantly rougher surface owing to the presence of several aliphatic groups . The side chains of branched amino acids such as Ile, Val, or Leu can interpenetrate these aliphatic spikes and are thus particularly suited for an association with the face of cholesterol through van der Waals interactions. This is the case for the cholesterol binding domain of -synuclein . Moreover, aromatic side chains can stack onto the face of cholesterol through CH- interactions . However, this should not be taken as an absolute rule since the aliphatic side chains of an -helical segment could also form a groove with a planar surface fitting the face of cholesterol . Conversely, an aromatic ring oriented normally with respect to the main axis of an -helical region could perfectly well accommodate the rough face of cholesterol by intercalating the aromatic structure between the aliphatic spikes of the lipid.
Read Also: Whats In Egg Beaters