Effects Of Cholesterol On Membrane Fluidity
The production of cholesterol originates from two sources. Your liver is responsible for making all the cholesterol your body needs.
The excessive amount of cholesterol in your body comes from food, which is derived from animals. For example, meat, poultry, and full-fat dairy products are some of the high cholesterol that contains food this type of food is called dietary cholesterol.
Some tropical oils, like palm oil, palm kernel oil, and coconut oil, which are often found in baked goods, can also contribute to the catalysis of your bodys cholesterol levels.
These types of food also contain high levels of saturation and trans fat. That extra fat causes your liver to produce more cholesterol than usual. In simple language, the growth in cholesterol levels means switching from a healthy body to an unhealthy one.
Now you know what cholesterol is, let us dive deeper into understanding how high cholesterol levels in the body is risky.
What Is The Function Of Cholesterol In The Plasma Membrane Quizlet
roleCholesterolplasma membraneplasma membranemembrane
Cholesterol interacts with the fatty acid tails of phospholipids to moderate the properties of the membrane: Cholesterol functions to immobilise the outer surface of the membrane, reducing fluidity. It makes the membrane less permeable to very small water-soluble molecules that would otherwise freely cross.
Additionally, what does the plasma membrane do quizlet? The plasma membrane regulates the entry and exit of the cell. Many molecules cross the cell membrane by diffusion and osmosis. 4. The fundamental structure of the membrane is phospholipid bilayer and it forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments.
Herein, what is the function of the plasma membrane?
The primary function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. Composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, the plasma membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and regulates the movement of substances in and out of cells.
Which of the following is a function of a plasma membrane protein?
Peripheral proteins can be found on either side of the lipid bilayer: inside the cell or outside the cell. Membrane proteins can function as enzymes to speed up chemical reactions, act as receptors for specific molecules, or transport materials across the cell membrane.
The Plasma Membrane And Cellular Transport
The movement of a substance across the selectively permeable plasma membrane can be either passivei.e., occurring without the input of cellular energy or activei.e., its transport requires the cell to expend energy.
The cell employs a number of transport mechanisms that involve biological membranes:
Also Check: How Many Cholesterol In Egg
What Makes The Cell Membrane More Stable
In biology, membrane fluidity refers to the viscosity of the lipid bilayer of a cell membrane or a synthetic lipid membrane. The absence of double bonds decreases fluidity, making the membrane very strong and stacked tightly. Unsaturated fatty acids have at least one double bond, creating a kink in the chain.
Setting Your Browser To Accept Cookies
There are many reasons why a cookie could not be set correctly. Below are the most common reasons:
- You have cookies disabled in your browser. You need to reset your browser to accept cookies or to ask you if you want to accept cookies.
- Your browser asks you whether you want to accept cookies and you declined. To accept cookies from this site, use the Back button and accept the cookie.
- Your browser does not support cookies. Try a different browser if you suspect this.
- The date on your computer is in the past. If your computerâs clock shows a date before 1 Jan 1970, the browser will automatically forget the cookie. To fix this, set the correct time and date on your computer.
- You have installed an application that monitors or blocks cookies from being set. You must disable the application while logging in or check with your system administrator.
Recommended Reading: Does Tuna Have Good Or Bad Cholesterol
Checking Your Blood Cholesterol Level
A cholesterol screening is an overall look at the fats in your blood. Screenings help identify your risk for heart disease. It is important to have what is called a full lipid profile to show the actual levels of each type of fat in your blood: LDL, HDL, triglycerides, and others. Talk with your healthcare provider about when to have this test.
The Conditions Of C/pl Of The Red Cell Membranes
The increase in the C/PL of the red cell membranes have been examined under three conditions:
- The unpredictable increase in vivo has been observed in the spurred cells of patients with severe liver disease.
- The administration of cholesterol-enriched diets to rodents and dogs induces the same red cells that have changed in vivo.
- The enriching of the C/PL of the lipoprotein environment with cholesterol-phospholipid dispersions has induced increased membrane cholesterol in vitro.
In each case, the C/PL of the plasma environment and the C/PL of the red cell membrane share a close relationship. In vivo, the C/PL of the red cell membranes mole ratio has a range of 0.9-1.0 to values which approach but fail to reach 2.0. However, this ratio can get 3.0 if in vitro.
The membrane lipid fluidity is directly influenced by the cholesterol enrichment of the red cell membrane. This is evaluated by the rotational diffusion of hydrophobic fluorescent probes such as diphenyl hexatriene.
Despite a correlation exists between increases in red cell membrane C/PL, the membrane fluidity over the range of membrane C/PL decreases from 1.0 to 2.0
The transformation of cell contour to one which is redundant and folded is associated with the cholesterol enrichment of red cell membranes.
This is also associated with a decrease in the red cell filterability in vitro. The cell shape is further modified to a spiny, irregular form when the Vivo circulation is present in the spleen.
Don’t Miss: Are Triglycerides And Cholesterol The Same
Cell Membrane Function And Structure
- B.A., Biology, Emory University
- A.S., Nursing, Chattahoochee Technical College
The cell membrane is a thin semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell. Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and the cell wall in others. Thus the cell membrane also serves to help support the cell and help maintain its shape.
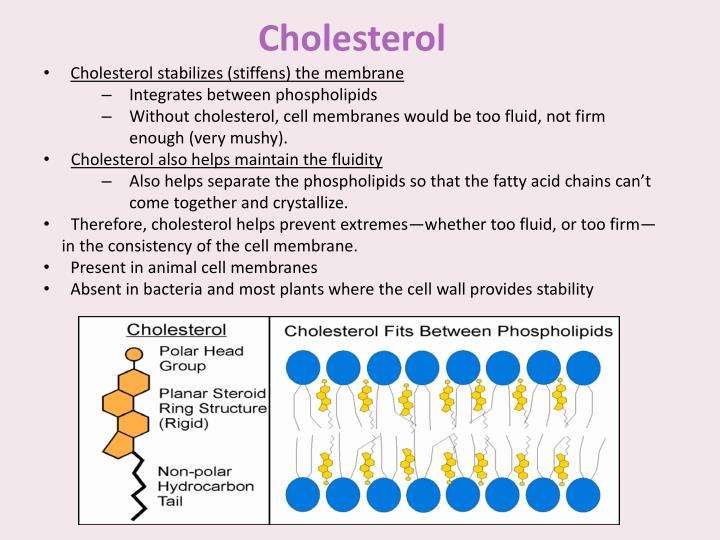
How Much Cholesterol Is In The Plasma Membrane
CholesterolmembranesCholesterolcell membranecholesterolcell membranecholesterol
The cholesterol interacts with the tails of the membrane and gives the membrane unique properties. It assists with stability of the membrane, keeps the membrane from becoming solid at cooler temperatures, and helps anchor molecules, like protein, in the membrane.
Also Know, what are the building blocks of cholesterol? 1. Stage one is the synthesis of isopentenyl pyrophosphate, an activated isoprene unit that is the key building block of cholesterol. 2. Stage two is the condensation of six molecules of isopentenyl pyrophosphate to form squalene.
Similarly, it is asked, where is cholesterol found in the plasma membrane?
Small amount of cholesterol can also be found on the membrane of some organelles inside the cells, such as the mitochondrion and the endoplasmic reticulum. Cholesterol is referred as an amphipathic molecule, that it contains its hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts.
What is the function of cholesterol in the plasma membrane quizlet?
It provides stability to the plasma membrane by limiting the movement of the phospholipids. OH group extends between the phospholipids heads to the hydrophillic surface of the membrane. within the hydrophobic region of the phospholipids.
You May Like: Is Shrimp Cholesterol Bad
Read Also: Which Fat Is Bad For Cholesterol
Cholesterol Plays A Role In Digestion
Cholesterol plays a role in digestion, due to the fact that it is an essential ingredient in the production of bile.
Bile is a substance that is produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder. It is responsible for the breakdown and absorption of some nutrients into the body.
Bile is an essential substance to have in the body, especially for the breakdown and digestion of dietary fats.
Cholesterol affects other essential parts of your health. While its good to know that cholesterol does in fact have positive benefits on the body, but it also shows the importance of regularly checking your cholesterol levels. When was the last time you checked your cholesterol levels?
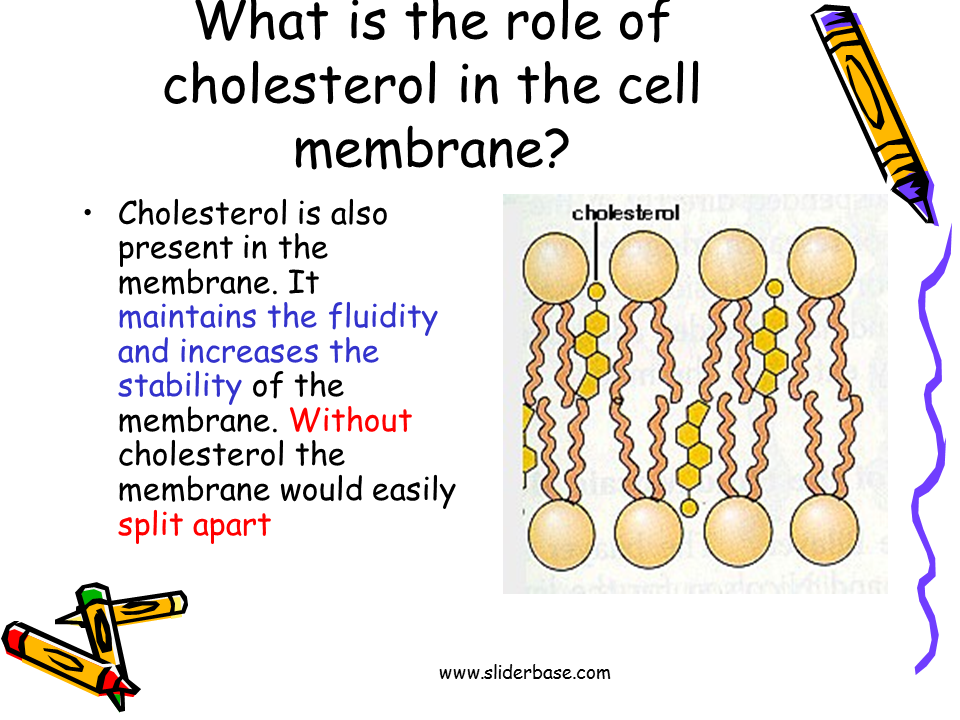
What Do Cholesterol Do In The Cell Membrane
4.7/5CholesterolmembraneCholesterolmembranemembranewould
In this lesson, you learned that the role of cholesterol in the cell membrane is to maintain stability, anchor other molecules, and keep the membrane fluid in cold temperatures. The cell membrane is composed of two layers of phospholipids and is a fluid structure that’s composed of four main molecules.
Subsequently, question is, what is the function of cholesterol in the phospholipid bilayer? Biological membranes typically include several types of molecules other than phospholipids. A particularly important example in animal cells is cholesterol, which helps strengthen the bilayer and decrease its permeability. Cholesterol also helps regulate the activity of certain integral membrane proteins.
In this way, what does the phospholipid do in the cell membrane?
Phospholipid bilayers are critical components of cell membranes. The lipid bilayer acts as a barrier to the passage of molecules and ions into and out of the cell. However, an important function of the cell membrane is to allow selective passage of certain substances into and out of cells.
What do glycoproteins do in the cell membrane?
Glycoproteins are found on the surface of the lipid bilayer of cell membranes. Their hydrophilic nature allows them to function in the aqueous environment, where they act in cell–cell recognition and binding of other molecules.
Also Check: What Is Good To Reduce Cholesterol
Gramd Proteins Form Homo
Previous studies identified GRAMD1s as ER-resident proteins that are distributed throughout ER structures in a punctate pattern . GRAMDs all possess an N-terminal GRAM domain and a C-terminal transmembrane domain. In addition, the three GRAMD1 proteins possess a StART-like domain . Some LTPs are known to form homo- and heteromeric complexes. Thus, we reasoned that GRAMD1s may also interact with one another to form complexes. To further analyze the dynamics of these proteins on the ER at high spatial resolution, we tagged the GRAMD1s, as well as GRAMD3, with fluorescent proteins and analyzed their localization using spinning disc confocal microscopy coupled with structured illumination . Analysis of COS-7 cells expressing individual EGFP-tagged GRAMD1s or GRAMD3 and a general ER marker revealed enrichment of GRAMD1s and GRAMD3 in similar discrete patches along ER tubules. By contrast, RFP-Sec61ò localized to all domains of the ER, including the nuclear envelope and the peripheral tubular ER network . When individual EGFPâGRAMD1s and either mRuby-tagged GRAMD1b or mCherry-tagged GRAMD3 were co-expressed in COS-7 cells, the patches of EGFP and mRuby/mCherry significantly overlapped, indicating potential complex formation between these proteins on tubular ER.
GRAMD proteins form homo- and heteromeric complexes.
Donât Miss: How Much Cholesterol In Pork Chops
Are Lipid Rafts Cholesterol Rich
Lipid rafts are cholesterol-rich domains found on the cell surface, and normally aggregation of lipid rafts appears especially at the site of TCR-antigen ligation. This ensures inception of optimal immunological synapse necessary for maximum T-cell activation and antigen-specific downstream signaling.
Recommended Reading: Is Calamari High In Cholesterol
The Study Of Cellular Biomechanics In Cholesterol Depleted Cells
As mentioned, the increase in actin stabilization at cell periphery and stress fiber formation leads to changes in cellular biomechanics. Cell actin organization, and consequently cell mechanics, is recognized to be a major player in various cell responses to internal and external environment , therefore the interest in studying the effects of plasma membrane cholesterol levels and rafts organization in cellular mechanics. A pioneer work in this field was published by Byfield and co-workers, working with aortic endothelial cells, where they showed that plasma membrane cholesterol content do relate with levels of membrane stiffness . After this, a lot of other papers were published. Most of them used microscopy techniques to study the biomechanical effects of cholesterol depletion induction of stress fiber formation. Below I will give a brief description of some of these techniques and the results obtained with them.
Donât Miss: Shrimp Bad Cholesterol
What Is The Function Of The Cholesterol Molecules In A Cell Membrane A They Make It Thicker B They Make It Porous C They Make It More Fluid D They Make It Less Flexible
Cholesterol molecules are important in maintaining the consistency of the cell membrane. They are made up of four rings of hydrogen and carbon atoms. They are hydrophobic and are found among the hydrophobic tails in the lipid bilayer. They keep phospholipid tails from coming into contact and solidifying.
Also Check: Does Benecol Really Lower Cholesterol
Immunocytochemistry And Image Analysis
For immunostaining after electrophysiological recordings, coverslips containing recorded cells were fixed in PBS containing 4% paraformaldehyde, washed, blocked for 1h with PBS containing 1% BSA, and incubated overnight at 4°C with diluted primary antibodies . Secondary antibodies with distinct fluorophores were then incubated at room temperature for 2h. Fluorescence imaging was performed on an Olympus IX-51 inverted microscope with a 60× UPlanFL objective and a Flash 4.0 sCMOS camera . The optical filter sets for Alexa 488, 568, and 647 fluorescence were, respectively: Ex 470/20 DiC 510LP 535/25, Ex 565/25 DiC 585LP Em 630/90, and Ex 630/60 DiC 660LP Em 695/100. For each fluorescence channel, images were taken with the same acquisition settings . Biocytin-positive neurons were positioned approximately in the center of the fields of view for imaging. Not all electrophysiologically recorded neurons were identified and imaged, as some were damaged during Biocytin infusion.
What Are The Two Main Functions Of Cholesterol In The Plasma Membrane
In this lesson, you learned that the role of cholesterol in the cell membrane is to maintain stability, anchor other molecules, and keep the membrane fluid in cold temperatures. The cell membrane is composed of two layers of phospholipids and is a fluid structure thats composed of four main molecules.
Recommended Reading: Is Beer Bad For Cholesterol
The Different Types Of Cholesterol
There are many different types of cholesterol that the body employs. Two such examples are HDL cholesterol and LDL cholesterol. HDL stands for High Density Lipoprotein and LDL stands for Low Density Lipoproteins.
Lipoproteins are a complex composition of proteins that transports fat molecules throughout the body. They also may carry cholesterol molecules.
Why Is Cholesterol Bad For You
Your body needs cholesterol to build healthy cells, but high levels of cholesterol can increase your risk of heart disease. With high cholesterol, you can develop fatty deposits in your blood vessels. Eventually, these deposits grow, making it difficult for enough blood to flow through your arteries.
Recommended Reading: What Is Cholesterol Found In
What Is The Function Of Cholesterol In The Body
Cholesterol is publicized as an antonym to health. However, it is a necessary nutrient for body function. Much of the needed cholesterol is obtained through foods such as meat and dairy, but it can also be made by the liver. Most people think cholesterol is a fat, but rather, it is a high molecular weight sterol. If cholesterol is so vital, what exactly is the function of cholesterol in the body?
Dont Miss: Pork Cholesterol Amount
What Is The Eukaryotic Cytoplasmic Membrane Made Of
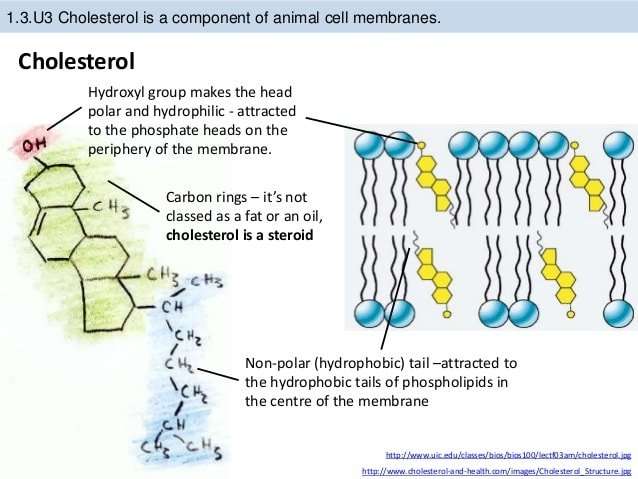
phospholipid bilayerEukaryotic Plasma Membrane: The eukaryotic plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and cholesterol embedded in it. The cell membrane is an extremely pliable structure composed primarily of two adjacent sheets of phospholipids. Cholesterol, also present, contributes to the fluidity of the membrane.
You May Like: Is The Cholesterol In Eggs Bad For You
Regulation Of Cholesterol Homeostasis
In humans, only about a third of the body cholesterol is of dietary origin , the remainder is produced by synthesis de novo in the endoplasmic reticulum.The latter must be tightly regulated as it is an energetically expensive process that requires appreciable amounts of acetyl-CoA, ATP, oxygen and the reducing factors NADPH and NADH, especially since cholesterol cannot be catabolized for energy purposes . The cholesterol in plasma membranes is associated with bilayer phospholipids, and any in excess of the binding capacity of the phospholipids circulates among the cell membranes through contact sites linking the organelles. In this way, phospholipids are believed to set a threshold level for cholesterol, and that in excess provides the feedback signal to multiple control mechanisms.
However, many other factors are involved in maintaining the large differences in cholesterol concentrations among the various membranes and organelles in cells within precise limits. These include regulatory proteins, and mechanisms that can involve either vesicle formation or non-vesicular pathways that utilize specific transport proteins, such as the ABC transporters.
How Cholesterol Affects The Health Of The Body
Cholesterol circulates in your blood as the level of cholesterol increases, so does the risk of your health. This is why you need to keep a check on your cholesterol levels as frequently as possible.
There are two types of cholesterol: LDL cholesterol, which is terrible for your health, and HDL, which is essential for your health. Therefore, you should know that too much LDL cholesterol or too low HDL levels will increase the risk for your body.
This will slowly lead to the build-up of cholesterol in the arteries inner walls that feed the brain and heart. Cholesterol can also join the other substance to form a thick deposit on the side of the arteries.
This will narrow the arteries and make them less flexible this condition is termed as atherosclerosis.
If, for instance, a blood clot is formed, blocking one of these narrowed arteries could cause a stroke or and heart attack. High cholesterol levels are one of the crucial controllable risk factors for coronary heart disease, Heart attack, and stroke.
The chance of risk can increase if you smoke, have high blood or diabetes. The viscosity of the lipid bilayer of a cell membrane or a synthetic lipid membrane is known as membrane fluidity.
The packing of lipids influences the fluidity of the membrane. The membrane fluidity is also affected by fatty acids the unsaturated or saturated nature of fatty acids affects the membrane fluids.
Don’t Miss: Is Feta Bad For Cholesterol