Lipid And Lipoprotein Metabolism
Lipids = cholesterol and triglyceride – are insoluble in plasma and are transported in lipoproteins.
Functions = energy utilization, steroid hormone production, bile acid production, lipid deposition.
Lipoprotein consists of esterified and unesterified cholesterol, triglycerides, phospholipids and apolipoproteins. The proteins function as cofactors and ligands for receptors.
Major lipoproteins include:
Exogenous pathway for lipid metabolism:
Endogenous pathway for lipid metabolism:
What Are The Types Of Lipoproteins
There are five main types of lipoproteins:
- High-density lipoprotein is the good cholesterol. It carries cholesterol back to your liver to be flushed out of your body. High levels of HDL reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Low-density lipoprotein is the bad cholesterol. It increases your risk of coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and strokes. LDL carries cholesterol that accumulates as plaque inside blood vessels. Plaque buildup can make blood vessels too narrow for blood to flow freely. This condition is atherosclerosis.
- Very low-density lipoproteins are another type of bad cholesterol. VLDLs carry triglycerides and to a less degree, cholesterol, to your tissues.
- Intermediate-density lipoproteins are created as VLDLs give up their fatty acids. They are then either removed by the liver or converted into LDL.
- Chylomicrons are very large particles that also transport triglycerides.
The Role Of Receptor Mediated Events In Fat Transport
Knowledge of the importance of lipoprotein receptors, which feature protein-protein interactions in the clearance of circulating lipoproteins, has modernized views of fat transport the pathways are shown in . As noted earlier, chylomicrons arise in the gut during fat digestion, enter the thoracic duct and then the blood stream where they are attacked by LPL, which reduces their triglyceride content by 75% and produces a chylomicron remnant that is taken up by B-100-E receptors on hepatocytes. Within the liver, the chylomicron remnant is decomposed to its amino acids and component lipids. Cholesterol released from lysosomes in hepatocytes can be excreted into bile, converted into bile acids, incorporated into VLDL for secretion into the blood via the Golgi apparatus or esterified with long-chain fatty acids and stored in the hepatocyte.
Receptor-mediated pathways of lipoprotein metabolism. Three major pathways are involved: chylomicrons, VLDL and HDL. Intermediate density lipoprotein is the remnant of VLDL and is cleared by the liver. LDL, which contains only apolipoprotein B-100, is the final product of the pathway most of it is returned to the liver. Some LDL is taken up by extrahepatic LDL receptors and some by a scavenger pathway. The apopeptides contained in each lipoprotein are indicated. Three plasma enzymes essential for lipoprotein metabolism include LPL , LCAT and HTGL
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take To Lower Cholesterol With Lipitor
Effects On Lipid Metabolism
HPMC modulates plasma lipoprotein profiles and hepatic lipid levels. HPMC is not absorbed by the body, but its presence in the intestinal lumen increases fecal fat, sterol, and bile acid excretion and as a result changes hepatic lipid metabolism. It has been suggested that HPMC may be facilitating fat excretion in a biased manner with preferential fecal excretion of both trans and saturated fats in hamsters fed with fast-food diets.
Derek G. Waller BSc , DM, MBBS , FRCP, Anthony P. Sampson MA, PhD, FHEA, FBPhS, in, 2018
Lipid Transport From The Liver
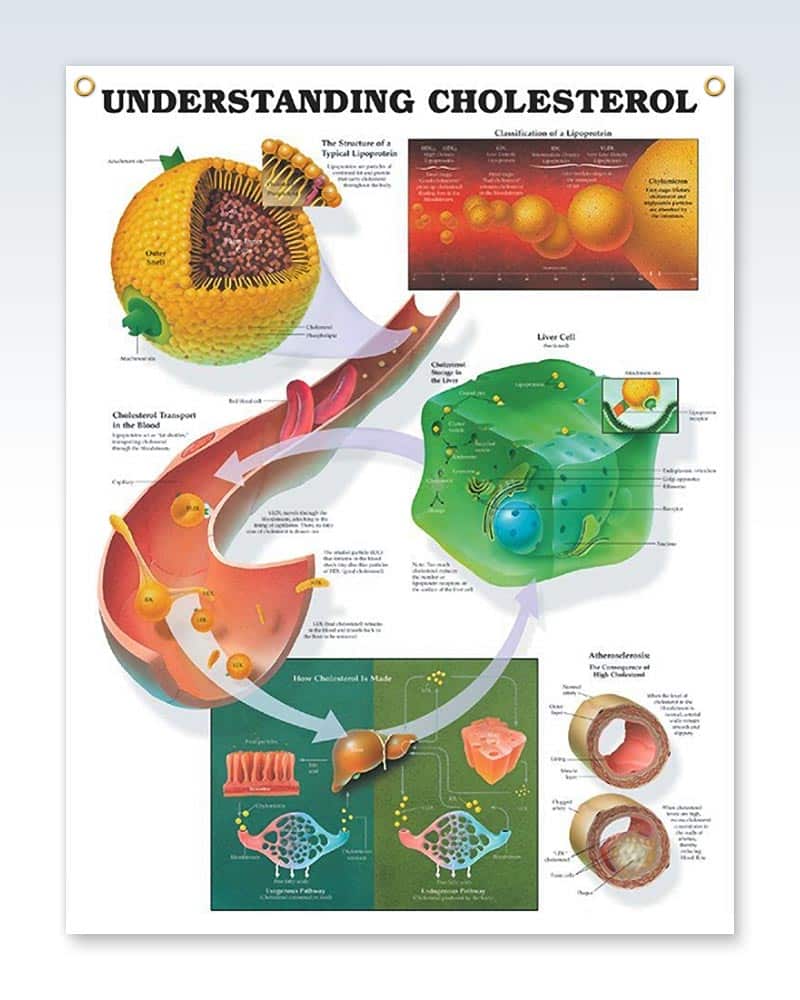
The contents of chylomicron remnants, as well as other lipids in the liver, are incorporated into another type of lipoprotein called very-low-density lipoprotein . Similar to chylomicrons, the main job of VLDL is delivering triglycerides to the bodys cells, and lipoprotein lipase again helps to break down the triglycerides so that they can enter cells .
As triglycerides are removed from VLDL, they get smaller and more dense, because they now contain relatively more protein compared to triglycerides. They become intermediate-density lipoproteins and eventuallylow-density lipoproteins . The main job of LDL is to deliver cholesterol to the bodys cells. Cholesterol has many roles around the body, so this is an important job. However, too much LDL can increase a persons risk of cardiovascular disease, as well discuss below.
High-density lipoproteins are made in the liver and gastrointestinal tract. Theyre mostly made up of protein, so theyre very dense. Their job is to pick up cholesterol from the bodys cells and return it to the liver for disposal.
Figure 5.27. Overview of lipoprotein functions in the body.
VIDEO: Cholesterol Metabolism, LDL, HDL, and Other Lipoproteins, Animation, by Alila Medical Media, YouTube , 3:45 minutes.
Recommended Reading: Eating Plan To Lower Triglycerides
Does Eating A Higher Fat Diet Mean You Will Store More Fat
No. How much fat a person stores depends on how many calories they consume relative to how many calories they need to fuel their body. If they consume more calories than needed to meet their bodys daily needswhether those calories come from dietary fat, carbohydrate, or proteinthen theyll store most of the excess calories in the form of fat in adipose tissue. If they consume a high-fat diet but not excess calories, then theyll utilize that fat to generate ATP for energy. That said, remember that fat is more calorically dense than protein or carbohydrates , so if you eat a high-fat diet, you may need to eat smaller portions. And, as well discuss later in this unit, there are good reasons to watch the type of fats that you eat, because of the relationship between dietary fat intake and risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
Lipid Transport Storage And Utilization
Once dietary lipids are digested in the gastrointestinal tract and absorbed from the small intestine, they need to be transported around the body so they can be utilized by cells or stored for later use. Once again, the fact that lipids arent water-soluble means that they need some help getting around the watery environment of the body. Lets take a look at how this works.
You May Like: What Is Normal Hdl Cholesterol Level For A Woman
Metabolomics Measurement Of The Phospholipids
Metabolomics analysis was performed at the Division of Metabolic and Nutritional Medicine of the Dr. von Hauner Childrenâs Hospital in Munich, Germany, by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry , as described previously .
The analysis of polar lipids comprised diacyl-phosphatidylcholines , acyl-alkyl-phosphatidylcholines , and SM. The analytical technique is not capable of determining the position of the double bonds and the distribution of carbon atoms between fatty acid side chains. The lipid species are described using the nomenclature CX:Y, where X is the length of the carbon chain , Y is the number of double bonds. âaâ means, that the acyl chain is bound via an ester bond to the backbone and âeâ means an ether bond.
For all metabolomics analyses, data acquisition on the mass spectrometer, data handling and quantification were performed with Analyst 1.6.2 software .
Also Check: Does Egg Beaters Have Cholesterol
Formation Of C15 And C30 Intermediates
The synthesis of the C15 intermediate, farnesyl-pyrophosphate, is catalyzed by the eponymous synthase and mechanistically resembles that of geranyl-pyrophosphate. Farnesyl-pyrophosphate is used not only in sterol synthesis but also in the posttranslational modification of some membrane-associated proteins. While the amount of farnesyl-pyrophosphate used for the latter purpose is not very large, inhibition of protein farnesylation may contribute to the clinical effect of inhibitory drugs that act upstream in this pathway this includes the statins, which inhibit HMG-CoA reductase .
Two molecules of farnesyl-pyrophosphate are joined head to head in the synthesis of the final linear sterol precursor, namely, squalene the enzyme is named squalene synthase.
11.2.5
Read Also: Does Oatmeal Help Lower Cholesterol
Is A Lipoprotein That Picks Up Cholesterol From Dying Cells And Other Sources And Transfers It To The Liver
High-density lipoproteins carry cholesterol from body tissues back to the liver where it can be removed from the body.
Which lipoprotein is responsible for picking up cholesterol and delivering it back to the liver quizlet?
HDL: picks up cholesterol from other lipoproteins and body cells and returns them to the liver to reuse or eliminate.
Which Lipoprotein Contains The Most Cholesterol Quizlet
VLDL has a mixture of lipids, most of which is triglycerides, and a small amount of proteins. The most cholesterol of all the lipoproteins is contained in this lipoprotein. It is composed of cholesterol, phospholipids and a small amount of other fatty acids. This is the main type of fat found in the body.
The main components of this fat are cholesterol and triglyceride, which are the two most common types of fats in our bodies. Cholesterol is a fat-soluble substance that can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Triglyceride is an unsaturated fatty acid that is found primarily in animal products, such as butter, cream, cheese and lard.
Both of these fats are considered to be bad fats because they are high in saturated fat and low in monounsaturated fat. This means that they can raise cholesterol levels and cause heart disease. However, they also have a number of health benefits, including reducing the risk of certain cancers, lowering blood pressure and helping to maintain a healthy weight.
In addition, both fats have been shown to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, as well as being a source of vitamins and minerals.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Cholesterol Deposits Under Eyes
Which Lipoprotein Transports Most Cholesterol Quizlet
high-density lipoprotein originates from the liver and small intestine.
What is RCT in biochemistry?
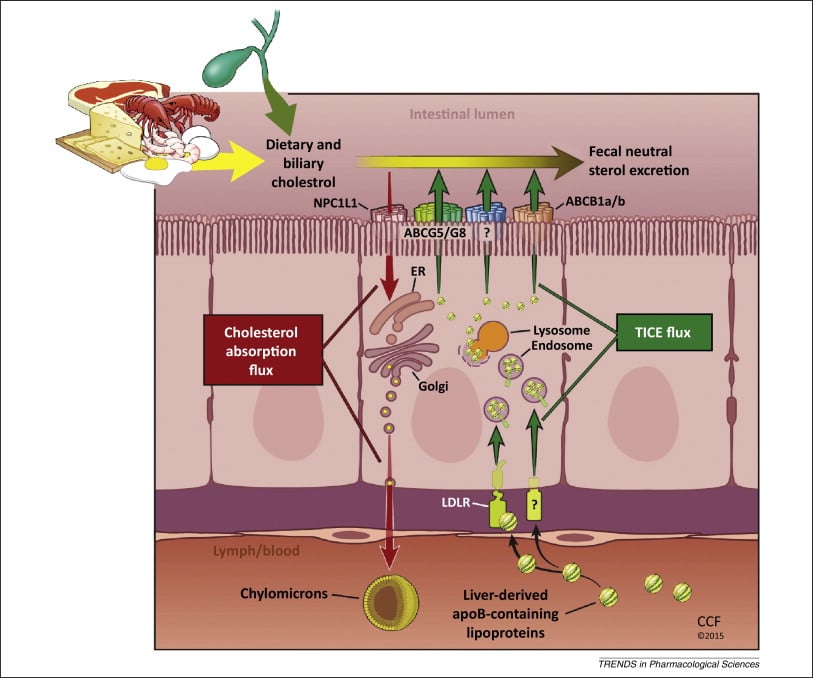
Reverse Cholesterol Transport RCT is the process by which excess cholesterol from non-hepatic tissues is transferred to the liver for metabolism and excretion into the bile.
Lipogenesis And Fatty Acid Synthesis
Lipogenesis is the process of synthesizing lipids as a means of storing chemical energy. Fat cells, or adipocytes, are dispersed throughout the body and are considered a long-term energy depot. Lipogenesis encompasses fatty acid synthesis , adipocyte uptake, and storage of lipids as the bodys savings account.
What Causes Fatty Acid Synthesis? Glucose is the key signal for fat storage . Excess energy generated from glycolysis and the TCA cycle is taken up by the body to convert it to fat. As ATP levels increase beyond the cells requirements, the ATP begins to accumulate, which stimulates activity of the enzyme acetyl CoA carboxylase. Increased insulin concentrations are also required to stimulate acetyl CoA carboxylase activity.
Fatty acid biosynthesis begins with 2 C acetyl CoA . Acetyl CoA could come from fats, carbohydrates, or some amino acids. Fatty acid synthesis occurs in the cytosol . The fatty acid chain is assembled in 2 C units by joining the carboxyl end of one fragment to the methyl tail of another, yielding palmitic acid as the end product.
You May Like: Are Pork Chops Heart Healthy
You May Like: Can Peanuts Cause High Cholesterol
Lipoprotein And Triacylglycerol Metabolism
Triacylglycerols are the most energy-dense molecules available to the body as a source of fuel but are highly hydrophobic. For efficient transport from the intestine and the liver to other organs of the body, it is essential that they be packaged in a form compatible with the aqueous environment in plasma, i.e., in lipoproteins. Chylomicrons and VLDL are mainly involved, although some proteins that are shared with HDL are essential for the process to function normally. For example, exchangeable apoproteins protect triacylglycerol-rich particles from non-specific interactions in plasma and ensure that they have the correct configuration to be acted upon by lipases.
After their release from lysosomes, the fatty acids and other lipid components serve as precursors for the synthesis of new lipidspecies and may also function in the regulation of many metabolic processes.For example, unesterified fatty acids are able to interact with the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor PPAR and so target gene expression.
It has been suggested that fatty acids released from VLDL triacylglycerols by lipoprotein lipase may act as signalling molecules to neurons and/or astrocytes in the brain, and these may in turn send information to peripheral tissues to maintain the energy balance at equilibrium.
What Is The Link With Triglycerides
Lipoproteins also carry triglycerides, the most common type of fat in the body.
Triglycerides store energy from food, but high triglyceride levels can be harmful, especially if a person has high LDL and low HDL levels.
If this happens, fatty substances can build up in the artery walls, increasing the risk of a stroke or heart attack.
An appropriate balance of lipoproteins and cholesterol is essential for health.
High levels of LDL and VLDL cholesterol are the development of atherosclerosis. In atherosclerosis, plaque builds up in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks, stroke, and heart disease.
Some types of LDL are also more dangerous than others. Small, dense LDL particles are to cause atherosclerosis than larger LDL particles.
This is because small, dense LDL particles circulate for longer and find it easier to enter and adhere to arteries. They are also more susceptible to oxidation, which happens when LDL interacts with unstable molecules called free radicals. High levels of free radicals can lead to damage and inflammation in the body.
HDL, meanwhile, helps remove excess cholesterol from the blood and protect against atherosclerosis.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Safe Cholesterol Level
Understanding Blood Cholesterol Numbers
A persons blood cholesterol numbers can be one indicator of their risk of developing cardiovascular disease. This is a standard blood test, also called a lipid panel, that reports total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and triglycerides. When doctors assess a persons risk of cardiovascular disease, they consider these numbersalong with other risk factors like family history, smoking, diabetes, and high blood pressurein determining their recommendations for lifestyle changes or prescribing medications.
You might be familiar with LDL and HDL as bad cholesterol and good cholesterol, respectively. This is an oversimplification to help people interpret their blood lipid values, because cholesterol is cholesterol its not good or bad. The cholesterol in your food or synthesized in your body is all the same cholesterol molecule, and you cant consume good or bad cholesterol. In reality, LDL and HDL are both lipoproteins that carry cholesterol. A more appropriate descriptor for LDL might be the bad cholesterol transporter. We can think of HDL as the good cholesterol transporter, although the more researchers learn about HDL, the more they realize that this is also an oversimplification.
- coronary artery disease
- carotid artery disease
- peripheral artery disease
- chronic kidney disease
Self-Check:
- University of Hawaii at Mnoa Food Science and Human Nutrition Program, Digestion and Absorption of Lipids, CC BY-NC 4.0
References:
Image Credits:
How To Improve Lipoprotein Levels
Various dietary and lifestyle modifications can impact lipoprotein levels and reduce the risk of disease.
If blood tests show that lipid levels are not within appropriate limits, a doctor will likely discuss the options for managing them.
Current recommendations for optimal blood lipid levels for adults aged 20 years and over are as follows:
- triglycerides: under 150 milligrams per deciliter
- LDL cholesterol: under 100 mg/dl
- HDL cholesterol: at least 40 mg/dl for males and 50 mg/dl for females
- total cholesterol: 125200 mg/dl
- non-HDL: less than 130 mg/dl
Below are some evidence-based ways to reach and maintain these optimal levels.
- Eating more fiber: A high-fiber diet can reduce LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels by 510%. Examples include beans, fruits, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
- Reducing excess body fat: This can HDL levels, decrease LDL and triglyceride levels, and help cut heart disease risk.
- Increasing physical activity: Exercise can help lower blood lipid levels, boost HDL levels, and may the concentration of small, dense LDL particles.
- Limiting added sugar and processed foods: Studies have unhealthy lipoprotein levels and high triglyceride levels.
- Cutting out processed meats: Studies have with unhealthy blood lipid levels.
- Choosing healthy fats: Fats from avocados, olive oil, nuts, and seeds improve blood lipid levels and decrease heart disease risk.
- Taking an omega-3 supplement:
Read Also: Which Cholesterol Drug Is Safest
The Characterization Of The Lipoprotein Apopeptides
Attempts were then made to identify the protein components of the major lipoproteins . They were delipidated with organic solvents and the resulting peptides fractionated and studied to determine their size, shape and amino acid composition. At first, there were difficulties from the insolubility of some of the peptides and the denaturation and/or proteolysis of others during isolation. Nonetheless, by the mid-1970s, it became clear that there were four families of peptides associated with the major lipoproteins. The A-apopeptides were associated primarily with the -lipoproteins the B-apopeptides with -lipoproteins and chylomicrons the migratory C-apopeptides with all lipoproteins except LDL and the E-apopeptide with VLDL, intermediate density lipoprotein and HDL . Most lipoprotein apopeptides are synthesized in the liver or the intestine, but one, apolipoprotein redundant E, is synthesized in all cells, except the gut.
Of particular importance for lipoprotein clearance are apo B-100 and apo E. Apo B-100, with 4536 amino acids and a molecular weight of 550 kDa is the largest protein known in mammals. Apo B-48, the form of apo B present in chylomicrons, is formed in the intestine from the same gene by mRNA editing. The mRNA for apo B-100 is truncated at residue 2152 to produce a smaller apo B devoid of its binding site to the LDL receptor.