What Causes Metabolic Syndrome
Experts don’t fully understand what causes metabolic syndrome. Several factors are interconnected. Obesity plus a sedentary lifestyle contributes to risk factors for metabolic syndrome. These include high cholesterol, insulin resistance, and high blood pressure. These risk factors may lead to cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
Because metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance are closely tied, many healthcare providers believe that insulin resistance may be a cause of metabolic syndrome. But they have not found a direct link between the two conditions. Others believe that hormone changes caused by chronic stress lead to abdominal obesity, insulin resistance, and higher blood lipids .
Other factors that may contribute to metabolic syndrome include genetic changes in a person’s ability to break down fats in the blood, older age, and problems in how body fat is distributed.
Data Collection And Definitions
Trained researchers interviewed participants in their homes using computer-assisted technology to collect sociodemographic information , health behavior , medical history and medication usage .
Anthropometric indicators included systolic blood pressure , diastolic blood pressure , body mass index , and waist circumference . Blood pressure were measured three times in a seated position by trained nurses using the HEM-7200 electronic monitor . Hypertension was defined as SBP140 mmHg or DBP 90 mmHg or self-reported prior diagnosis of hypertension by a doctor or using antihypertensive drugs in the past 2 weeks . Height and WC measurement were accurate to 0.1 cm and 0.1 kg, respectively.
These samples were transported from all study sites to Beijing and were stored at 80°C at the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. The determination of FBG, Hemoglobin A1c, TG, total cholesterol , low-density lipoprotein cholesterol , and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol were conducted by trained research staff. TyG index was calculated as ln . At baseline and follow-up, diabetes was defined as FBG > 125 mg/dL or Hemoglobin A1c > 6.5%, self-reported prior diagnosis of diabetes by a doctor or using antidiabetic medications. Participants whose FBG was at 100125 mg/dL or Hemoglobin A1c was at 5.76.4% were classified as having prediabetes . Participants without diabetes or prediabetes were defined as normoglycemia.
Statins And New Onset Diabetes
It was first observed in the JUPITER trial that patients receiving high dose rosuvastatin have a higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes compared to those receiving placebo . This contrasted with earlier studies were no such effect or even a protective effect was observed . Following the WOSCOP study a number of smaller trials tried to clarify the effect of statins on insulin resistance and insulin secretion without giving clear results .
After the JUPITER trial many data sets were reanalyzed and it was shown that the risk for new onset diabetes is increased with statin therapy. The increased incidence was confirmed in the Women’s Health Initiative and also in a Finish observational study evaluating almost 8,500 nondiabetic men as well as in a number of meta-analyses. One such meta-analysis evaluated whether reaching certain LDL-C levels is associated with an increased risk for type 2 diabetes. It was shown that the OR for developing diabetes is 1.33 in those reaching an LDL-C < 70 mg/dL , while the OR is 1.16 in those achieving an LDL-C between 70 and 100 mg/dL and not elevated in those with LDL-C above 100 mg/dL . Further analyses then indicated that the risk for new onset diabetes holds probably true for all statins and occurs in a dose dependent fashion .
You May Like: Which Component In The Accompanying Figure Is Cholesterol
Oral Glucose Tolerance Tests Can Help Diagnose Insulin Resistance
An OGTT or oral glucose tolerance test remains the current gold standard to diagnose insulin resistance or hyperinsulinemia. During that test, we give you a drink with 75 grams of glucose. Then we check your glucose and insulin levels at 30-minute intervals afterward. Many people who have an OGTT will be shown to have insulin resistance. Their glucose will be elevated above what it should be, and more importantly, the amount of insulin in your blood needed to decrease that glucose level by driving the glucose into your muscle and liver will be increased.
Researchers at Yale have found evidence of insulin resistance in 30-40% of thin, healthy appearing college student volunteers when subjected to an OGTT.
Ok lets keep going. Lets say you havent had an OGTT.
Now we are going to discuss:
- Why the Triglyceride/HDL ratio helps predict risk and once you understand that,
- What you can do to improve that ratio and decrease your odds of living with diseases associated with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia.
Research Articleinsulin Resistance Is Associated With Increased Cholesterol Synthesis And Decreased Cholesterol Absorption In Normoglycemic Men
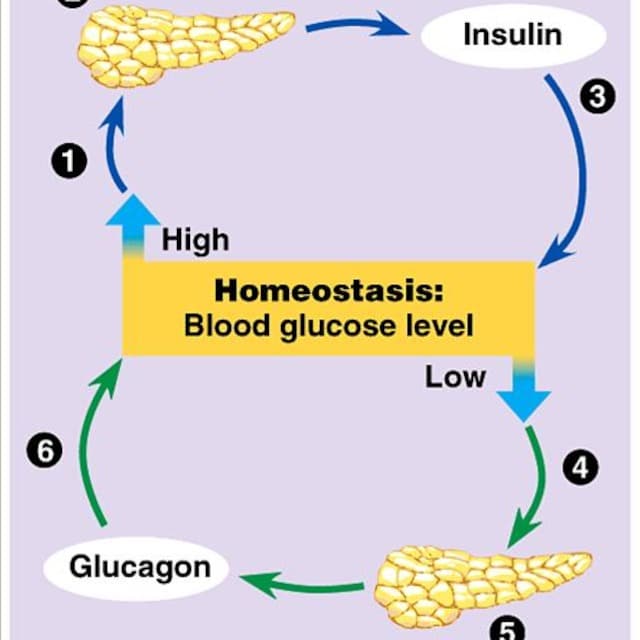
Type 2 diabetes has been associated with high synthesis and low absorption of cholesterol independent of weight, indicating that insulin resistance may be a link between glucose and cholesterol metabolism. Therefore, we investigated the relationship of serum cholesterol precursors, reflecting cholesterol synthesis, and serum plant sterols and cholestanol, reflecting cholesterol absorption efficiency, with insulin sensitivity measured with the hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp in 72 healthy normoglycemic men. Men in the most insulin-resistant tertile had higher serum cholesterol precursor ratios , whereas no significant differences in serum absorption sterols were observed. In bivariate analysis, cholesterol synthesis markers correlated with fasting insulin and the rates of insulin-stimulated whole-body glucose uptake . Also, cholesterol absorption markers correlated with fasting insulin and WBGU . Fasting insulin correlated with desmosterol and lathosterol even when the rates of WBGU and body mass index were controlled for.
We conclude that insulin resistance is linked to high cholesterol synthesis and decreased cholesterol absorption. Because fasting insulin correlated with cholesterol synthesis independent of the rates of BMI and WBGU, it is possible that regulation of cholesterol synthesis by hyperinsulinemia may be a link between insulin resistance and cholesterol metabolism.
Read Also: Is Potato Good For Cholesterol
Who Is At Risk For Metabolic Syndrome
Knowing your risk factors for any disease can help guide you to take the appropriate actions. This includes changing behaviors and being monitored by your healthcare provider for the disease.
Risk factors most closely tied to metabolic syndrome include:
- Age. You are more likely to have metabolic syndrome the older you are.
- Ethnicity. African Americans and Mexican Americans are more likely to get metabolic syndrome. African-American women are about 60% more likely than African-American men to have the syndrome.
- Body mass index greater than 25. The BMI is a measure of body fat compared with height and weight.
- Personal or family history of diabetes. Women who have had diabetes during pregnancy or people who have a family member with type 2 diabetes are at greater risk for metabolic syndrome.
Here are the types of treatment that may be recommended for metabolic syndrome.
Study Design And Participants
Data for our analysis were from the China H-type Hypertension Registry Study . The CHRS study is an observational, real-world, ongoing prospective cohort study evaluating the treatment, related risk factors and prognosis of patients with hypertension in Wuyuan, Jiangxi Province, China. The study protocol and informed consent were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Anhui Medical University Biomedical Institute. All participants signed the written informed consent form.
The study design and methods of data collection have been described in detail previously.23 Briefly, from March 2018 to August 2018, a total of 14,268 hypertensive patients in the community were enrolled in the CHRS study. At each visit site, face-to-face interviews via a structured questionnaire, anthropometric measurements, and collection of blood samples were completed at baseline. The follow-up investigation was conducted from 31 August 2018 to 31 March 2020, and 14,227 individuals remained in the cohort. We excluded 4324 participants who were younger than 60 years old. After the exclusion of 750 participants with a history of stroke, 459 patients using glucose-lowering drugs, 201 patients using lipoprotein-lowering drugs, and 6 participants without data on the TyG index, a total of 8487 elderly hypertensive patients were selected for the final analysis .
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Drink To Lower Cholesterol
Familial Hypercholesterolemia And Type 2 Diabetes
In recent years patients with familial hypercholesterolemia have returned into the focus of lipidology . Familial hypercholesterolemia can be caused by mutations affecting the LDL-receptor gene, the gene encoding apolipoprotein B, the protein binding to the LDL-receptor, or the gene encoding PCSK9, a regulator of LDL-receptor recycling . All mutations result in a decreased catabolism of LDL-particles through the LDL-receptor. The decreased catabolism of LDL directly translates into elevated LDL-C levels. The elevated cholesterol levels are causally linked to cardiovascular disease. In addition, the elevated concentration of plasma lipoproteins can result in the deposition of lipids in a number of other organs resulting in the formation of xanthomas and arcus lipoides. Thus, patients with familial hypercholesterolemia are characterized by elevated LDL-C plasma concentration, premature cardiovascular disease, skin manifestation and usually a strong positive family history for hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerotic disease. The risk for cardiovascular events in affected individuals is approximately 10 to 20 folds higher than in those not affected . A number of studies have shown that LDL-C lowering therapy with statins can dramatically improve the prognosis of these subjects . It is therefore recommended that statin therapy is initiated early in life with some variation depending on the LDL-C level, the family history and the presence of additional risk factors .
Diabetes And Your Heart
You can lower your risk for heart disease with lifestyle changes.
Diabetes and heart disease often go hand in hand. Learn how to protect your heart with simple lifestyle changes that can also help you manage diabetes.
Heart disease is very common and serious. Its the leading cause of death for both men and women in the United States. If you have diabetes, youre twice as likely to have heart disease or a stroke than someone who doesnt have diabetesand at a younger age. The longer you have diabetes, the more likely you are to have heart disease.
But the good news is that you can lower your risk for heart disease and improve your heart health by changing certain lifestyle habits. Those changes will help you manage diabetes better too.
Read Also: Are Olives High In Cholesterol
How Does Diabetes Affect Cholesterol
Diabetes tends to lower “good” cholesterol levels and raise triglycerides and “bad” cholesterol levels, which increases the risk for heart disease and stroke. This condition is called diabetic dyslipidemia.
Diabetic dyslipidemia means your lipid profile is going in the wrong direction. It’s a combination that puts people at risk for premature coronary heart disease and atherosclerosis.
Studies show a link between insulin resistance, which is a precursor to Type 2 diabetes, and diabetic dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis and blood vessel disease. These conditions can develop even before diabetes is diagnosed.
How Diabetes Affects Your Heart
Over time, high blood sugar can damage blood vessels and the nerves that control your heart. People with diabetes are also more likely to have other conditions that raise the risk for heart disease:
- High blood pressure increases the force of blood through your arteries and can damage artery walls. Having both high blood pressure and diabetes can greatly increase your risk for heart disease.
- Too much LDL cholesterol in your bloodstream can form plaque on damaged artery walls.
- High triglycerides and low HDL cholesterol or high LDL cholesterol is thought to contribute to hardening of the arteries.
None of these conditions has symptoms. Your doctor can check your blood pressure and do a simple blood test to see if your LDL, HDL, and triglyceride levels are high.
These factors can also raise your risk for heart disease:
- Being overweight or having obesity
- Not getting enough physical activity
- Eating a diet high in saturated fat, trans fat, cholesterol, and sodium
- Drinking too much alcohol
People with diabetes are also more likely to have heart failure. Heart failure is a serious condition, but it doesnt mean the heart has stopped beating it means your heart cant pump blood well. This can lead to swelling in your legs and fluid building up in your lungs, making it hard to breathe. Heart failure tends to get worse over time, but early diagnosis and treatment can help relieve symptoms and stop or delay the condition getting worse.
Recommended Reading: How To Lower Cholesterol Levels For Blood Test
Living With Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a lifelong condition that will require changes in your lifestyle. If you already have heart disease or diabetes, follow your healthcare providers recommendations for managing these conditions.
Lifestyle changes involved in managing metabolic syndrome include:
- Stopping smoking if youre a smoker or use other tobacco products
- Losing weight if you are overweight or obese
How To Lower Triglyceride Levels
There are some steps that you can take to try to lower your triglyceride levels. Here are a few ideas recommended by the American Heart Association.
- Exercise regularly.
- Eat a diet that’s low in carbohydrates, sugar, saturated fat, and trans fat.
- Include heart-healthy fats in your diet .
- Quit smoking or using tobacco products.
- Limit your alcohol intake.
- Get and keep your blood sugars within your target range.
If lifestyle changes don’t help get your triglyceride levels down, talk to your healthcare provider. You might need to take medications or supplements to help lower your triglyceride levelsespecially if they’re high because of genetics.
You May Like: Are Cholesterol And Diabetes Related
What Is Heart Disease
Heart disease includes several kinds of problems that affect your heart. The term cardiovascular disease is similar but includes all types of heart disease, stroke, and blood vessel disease. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which affects blood flow to the heart.
Coronary artery disease is caused by the buildup of plaque in the walls of the coronary arteries, the blood vessels that supply oxygen and blood to the heart. Plaque is made of cholesterol deposits, which make the inside of arteries narrow and decrease blood flow. This process is called atherosclerosis, or hardening of the arteries. Decreased blood flow to the heart can cause a heart attack. Decreased blood flow to the brain can cause a stroke.
Hardening of the arteries can happen in other parts of the body too. In the legs and feet, its called peripheral arterial disease, or PAD. PAD is often the first sign that a person with diabetes has cardiovascular disease.
Mismanaged Type 2 Diabetes
One of the most common chronic illnesses in the United States is type 2 diabetes. The CDC estimates that 37.3 million Americans have it, and as many as 96 million are pre-diabetic. Studies have shown that high triglyceride levels have links to poor blood glucose control. If you have diabetes and donât correctly manage it, you may find your triglyceride levels climbing, potentially worsening your diabetes. So, controlling your triglyceride levels may help you handle type 2 diabetes.
Recommended Reading: Should You Fast Before A Cholesterol Test
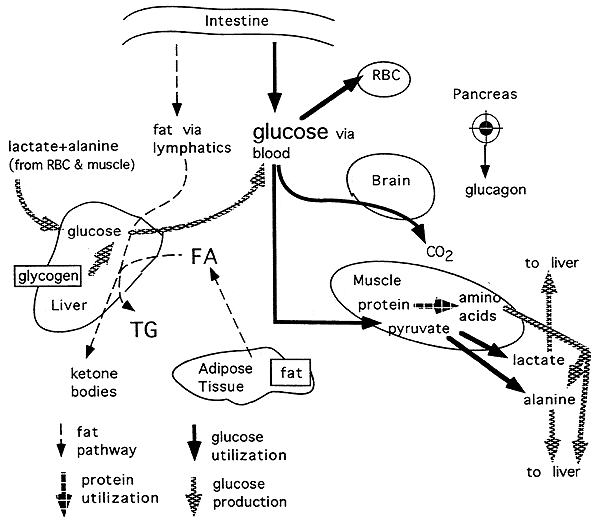
Triglycerides And Sugar Why Sugary Foods Should Be Avoided
Triglycerides are fats in the blood and in normal and healthy amounts they contribute to many vital physiological processes. For instance, they are used to transport necessary cholesterol throughout the body and they are also used for energy and they are helpful in storing it as well. But, in great abundance, they can be problematic and dramatically increase the risk for heart disease and resulting complications. While the lipids are very much associated with fats, triglycerides and sugar are also just as intimately related. In fact, sugar avoidance is one of the major factors to maintaining proper triglycerides levels.
When simple sugars are consumed, the body very quickly gobbles them up and converts them into energy, which leads to an instant spike in glucose levels, prompting the pancreas to begin releasing insulin. However, excess sugars that are not immediately used are stored. A maximum capacity for glycogen storage however can result in the liver converting this excess glucose into triglycerides. This can lead to a very rapid increase in the blood lipids, even causing the blood to become milky inconsistency. It is in this way that triglycerides and sugar are so closely related.
References:
Baseline Characteristics Of Study Participants
The baseline characteristics of all participants according to quartiles of TyG index and the proportion of diabetes development were summarized in Tables 1, 2, respectively. The present study included 7,428 participants . The mean value TyG index was 8.56. Among quartiles of TyG index, we observed significant differences in all baseline covariates except for marriage status and education level . When compared with participants without diabetes during follow-up, subjects who developed diabetes were older in age, having lower education level, less likely to be married, having higher levels of SBP, DBP, BMI, WC, TG, TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, FBG, Hemoglobin A1c, and TyG index, more likely to have hypertension and CVD, and more likely to use lipid-lowing drugs .
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of study participants according to quartiles of triglyceride glucose index.
Table 2. Comparison of baseline characteristics of study participants who developed diabetes or not.
Read Also: Is Cheese Bad For Your Cholesterol
Take Care Of Your Heart
These lifestyle changes can help lower your risk for heart disease or keep it from getting worse, as well as help you manage diabetes:
- Follow a healthy diet. Eat more fresh fruits and vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains. Eat fewer processed foods and avoid trans fat. Drink more water, fewer sugary drinks, and less alcohol.
- Aim for a healthy weight. If youre overweight, losing even a modest amount of weight can lower your triglycerides and blood sugar. Modest weight loss means 5% to 7% of body weight, just 10 to 14 pounds for a 200-pound person.
- Get active. Being physically active makes your body more sensitive to insulin , which helps manage your diabetes. Physical activity also helps control blood sugar levels and lowers your risk of heart disease. Try to get at least 150 minutes per week of moderate-intensity physical activity, such as brisk walking.
- Manage your ABCs:
- A: Get a regular A1C test to measure your average blood sugar over 2 to 3 months aim to stay in your target range as much as possible.
- B: Try to keep your blood pressure below 140/90 mm Hg .
- C: Manage your cholesterol levels.
- s: Stop smoking or dont start.