What Is Insoluble Fiber
Insoluble fiber is generally referred to as “roughage.” Insoluble fiber promotes regularity, adds bulk and softness to stools, helps with weight regulation and helps prevent many gastrointestinal disorders. Good sources on insoluble fiber include:
- Wheat bran and whole wheat or grain bread/bread products, pasta, cereal and crackers.
- Vegetables.
- Nuts.
Metabolism Recycling And Excretion
Cholesterol is susceptible to oxidation and easily forms oxygenated derivatives called oxysterols. Three different mechanisms can form these: autoxidation, secondary oxidation to lipid peroxidation, and cholesterol-metabolizing enzyme oxidation. A great interest in oxysterols arose when they were shown to exert inhibitory actions on cholesterol biosynthesis. This finding became known as the “oxysterol hypothesis”. Additional roles for oxysterols in human physiology include their participation in bile acid biosynthesis, function as transport forms of cholesterol, and regulation of gene transcription.
In biochemical experiments radiolabelled forms of cholesterol, such as tritiated-cholesterol are used. These derivatives undergo degradation upon storage and it is essential to purify cholesterol prior to use. Cholesterol can be purified using small Sephadex LH-20 columns.
Although cholesterol is a steroid generally associated with mammals, the human pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis is able to completely degrade this molecule and contains a large number of genes that are regulated by its presence. Many of these cholesterol-regulated genes are homologues of fatty acid-oxidation genes, but have evolved in such a way as to bind large steroid substrates like cholesterol.
How Much Is Too Much Saturated Fats
Most foods you choose should contain no more than 2 grams of saturated fat per serving. To help lower your LDL cholesterol, no more than 5 to 6 percent of your daily calorie intake should come from saturated fats. Use the list below to figure out the maximum amount of saturated fat you can have each day.
- Daily Calories:1,200
- Daily Saturated Fat Limit : 7-8g
Recommended Reading: Does Egg Beaters Contain Eggs
Limiting Saturated And Trans Fats
Here are some ways to lower your intake of saturated and trans fats:
- Maintain a diet that emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, low-fat dairy products, poultry, fish and nuts. Also limit red meat and sugar-sweetened foods and beverages.
- Opt for naturally occurring unhydrogenated vegetable oils such as canola, safflower, sunflower or olive oil.
- Look for processed foods made with unhydrogenated oil rather than saturated fat or hydrogenated vegetable oils.
- Use soft margarine as a substitute for butter and choose soft margarines over harder stick forms. Look for 0 g trans fat on the Nutrition Facts label.
- Doughnuts, cookies, crackers, muffins, pies and cakes are examples of foods high in trans fat. Dont eat them often.
- Limit commercially fried foods and baked goods made with shortening or partially hydrogenated vegetable oils. These foods are very high in fat, and its likely to be trans fat.
- Limit fried fast food. Commercial shortening and deep-frying fats are still made by hydrogenation and contain saturated and trans fats.
Consider using a food diary to keep track of what you eat. Its a handy way to evaluate the healthy, not-so-healthy and unhealthy foods youre making a part of your everyday diet.
Regulation Of Cholesterol Synthesis
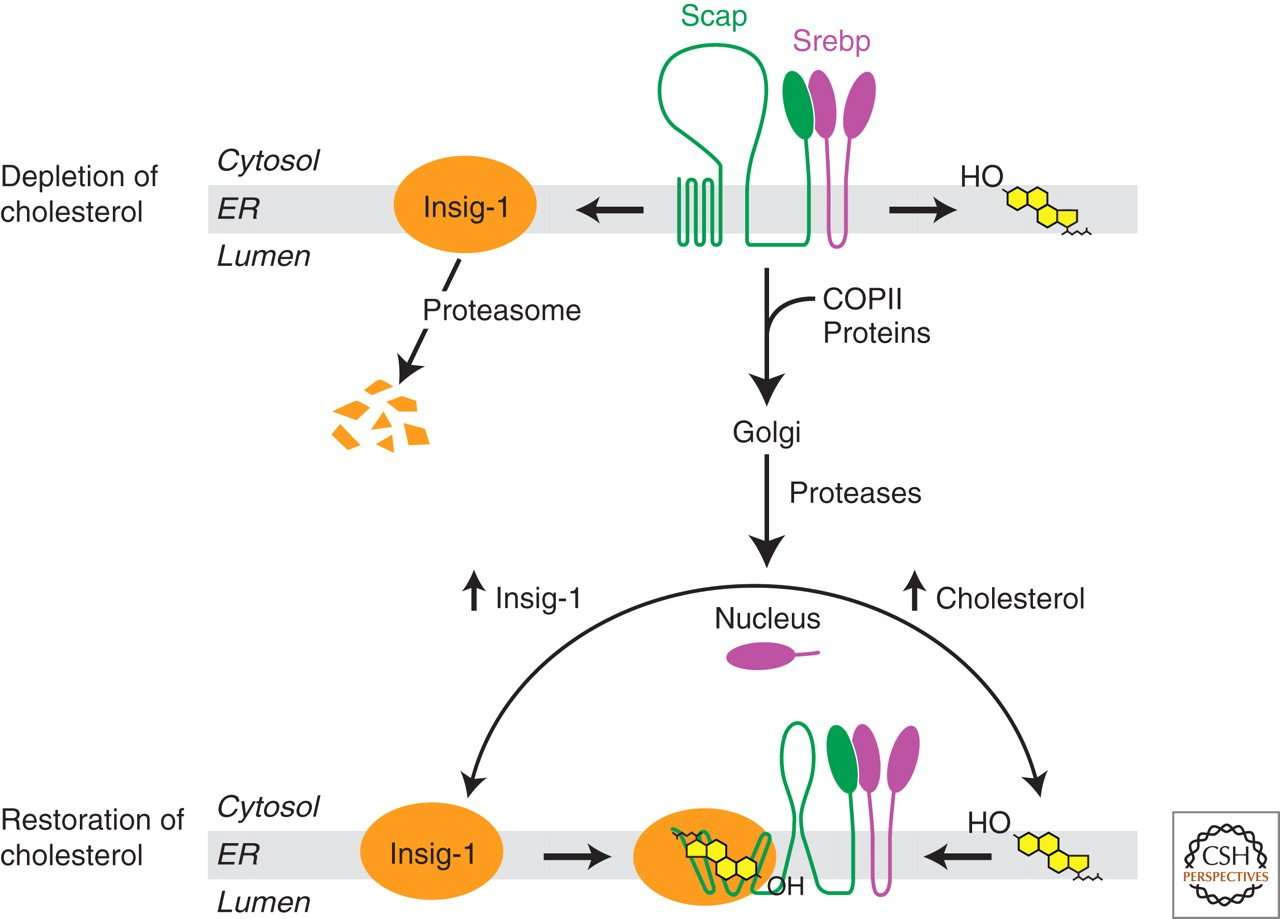
Biosynthesis of cholesterol is directly regulated by the cholesterol levels present, though the homeostatic mechanisms involved are only partly understood. A higher intake from food leads to a net decrease in endogenous production, whereas lower intake from food has the opposite effect. The main regulatory mechanism is the sensing of intracellular cholesterol in the endoplasmic reticulum by the proteinSREBP . In the presence of cholesterol, SREBP is bound to two other proteins: SCAP and INSIG-1. When cholesterol levels fall, INSIG-1 dissociates from the SREBP-SCAP complex, which allows the complex to migrate to the Golgi apparatus. Here SREBP is cleaved by S1P and S2P , two enzymes that are activated by SCAP when cholesterol levels are low.
Cholesterol synthesis can also be turned off when cholesterol levels are high. HMG-CoA reductase contains both a cytosolic domain and a membrane domain. The membrane domain senses signals for its degradation. Increasing concentrations of cholesterol cause a change in this domain’s oligomerization state, which makes it more susceptible to destruction by the proteasome. This enzyme’s activity can also be reduced by phosphorylation by an AMP-activated protein kinase. Because this kinase is activated by AMP, which is produced when ATP is hydrolyzed, it follows that cholesterol synthesis is halted when ATP levels are low.
Also Check: Is Shrimp Bad For Your Cholesterol
Checking Your Blood Cholesterol Level
A cholesterol screening is an overall look at the fats in your blood. Screenings help identify your risk for heart disease. It is important to have what is called a full lipid profile to show the actual levels of each type of fat in your blood: LDL, HDL, triglycerides, and others. Talk with your healthcare provider about when to have this test.
Why Do We Need Cholesterol
Cholesterol plays a vital role in how your body works. There is cholesterol in every cell in your body, and it’s especially important in your brain, nerves and skin.
Cholesterol has three main jobs:
- Its part of the outer layer, or membrane, of all your bodys cells
- Its used to make vitamin D and steroid hormones which keep your bones, teeth and muscles healthy
- Its used to make bile, which helps to digest the fats you eat
Also Check: Feta Cheese And Cholesterol
Dha Versus Epa On Blood Lipids
The improvements in LDL density with the consumption of marine omega-3s seem to be largely from DHA, which, when compared with EPA, increases LDL particle size and reduces sdLDL particles. However, supplementation with purified EPA has also been found to reduce sdLDL, remnant lipoproteins and lower inflammation in patients with metabolic syndrome. Thus, DHA may simply be better than EPA at providing beneficial changes in LDL particle size and/or density. In one study of 74 healthy normolipidaemic men and women 2.3 g of DHA per day, but not 2.2 g of EPA, significantly increased HDL levels by 13% . This may have been due to the twofold greater reduction in fasting triacylglycerol with DHA versus EPA.
Another group of authors concluded that despite DHA being found in lower concentrations compared with EPA in many supplements, DHA has equally important antiarrhythmic, antithrombotic and antiatherogenic effects. One randomised study of 38 dyslipidaemic patients showed that DHA reduced TG levels more than EPA as compared with placebo . Both omega-3 fatty acids improved systemic arterial compliance.
Medical Guidelines And Recommendations
In 2016, the United States Department of Agriculture Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee recommended that Americans eat as little dietary cholesterol as possible, because most foods that are rich in cholesterol are also high in saturated fat and thereby may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. Previously, the Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommended that dietary cholesterol be no more than 300 mg per day. The DGAC dropped this recommendation because evidence showed no appreciable relationship between dietary and serum cholesterol, consistent with the 2013 report by the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology. Although there is a link between cholesterol and atherosclerosis, a 2014 review concluded there is insufficient evidence to support the recommendation of high consumption of polyunsaturated fatty acids and low consumption of total saturated fats for cardiovascular health.
Some supplemental guidelines have recommended doses of phytosterols in the 1.63.0 grams per day range . A recent meta-analysis demonstrating a 12% reduction in LDL-cholesterol at a mean dose of 2.1 grams per day. However, the benefits of a diet supplemented with phytosterols have also been questioned.
| > 6.2 | High risk |
Also Check: Are Bananas Good For High Cholesterol
How Does Cholesterol Affect Membrane Fluidity Importance Of Membrane Fluidity
Maintaining membrane fluidity is extremely vital for the continues existence of the cell as it provides it with continuous protection. For instance, if you insert a needle into a cell membrane, it will penetrate without causing it to burst and once the needle is removed, the membrane will seamlessly self-seal. Other reasons why membrane fluidity is important include, allowing membrane fusion guarantying equal distribution in membrane molecules enabling separation of the membrane during cell division, and many others.
Factors Affecting Membrane Fluidity
Cell membrane fluidity can be affected by multiple factors and depends in large part on its lipids composition. Some of the factors that can affect membrane fluidity are:
Degree of Fatty Acids Saturation
Fatty acids can have saturated or unsaturated tails. Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds, for this reason, they are relatively straight. On the other hand, unsaturated fatty acids contain one or more double bonds and as a result they are crooked.
Due to this bending effect, unsaturated fatty acids increase fluidity, while saturated fatty acids increase rigidity in the cell membrane.
Length of the Fatty Acids Tail
The longer the fatty acid tail the more rigid the membrane will be. On the contrary, short length fatty acids can potentially increase cell membrane fluidity.
Temperature
How does Cholesterol increase or decrease flexibility of the membrane?
How Is High Cholesterol Diagnosed
There are usually no signs or symptoms that you have high cholesterol. There is a blood test to measure your cholesterol level. When and how often you should get this test depends on your age, risk factors, and family history. The general recommendations are:
For people who are age 19 or younger:
- The first test should be between ages 9 to 11
- Children should have the test again every 5 years
- Some children may have this test starting at age 2 if there is a family history of high blood cholesterol, heart attack, or stroke
For people who are age 20 or older:
- Younger adults should have the test every 5 years
- Men ages 45 to 65 and women ages 55 to 65 should have it every 1 to 2 years
You May Like: Are Baked Potatoes High In Cholesterol
Fatty Acids Profile Of Egg Edible Parts And Yolk
A part of the lipid was extracted from whole edible part of egg and yolk was analyzed for its fatty acid contents by gas liquid chromatography using Shimadzu Gas Chromatograph GC-4CM . A standard mixture of methyl esters was analyzed under identical conditions prior to running the samples. The instrument was equipped with flame ionization detector under the following conditions: an analytical glass column packed with 5 % diethylene glycol succinate on 80/100 Chromo Q. Operating temperature for column: 180 °C isothermal and injector and detector: 270 °C and gas flow rates for nitrogen: 30, hydrogen: 1, and air: 0.5. Chart speed 0.5 mm/min according to . The retention times of the unknown sample of methyl esters was compared with those of the standard. The concentration of methyl esters was calculated by the triangulation method.
Total antioxidant capacity and malondialdehyde determinations for the whole edible of eggs were performed using diagnostic kits , according to the method given by , respectively.
Atherogenic and thrombotic indices:
Atherogenic and thrombogenic indices were calculated using the equations as follows:
where MUFA is monounsaturated fatty acids.
What Are Triglycerides
ByJessie Szalay24 March 2016
Triglycerides are a type of fat found in the blood. They are the most common type of fat in the body. Triglycerides are necessary for health but in excess amounts, they may be harmful and may increase the risk of heart disease. For this reason, scientists think that triglyceride levels may be an important measure of metabolic health.
“When you eat more calories than you need, the body stores those calories in the form of triglycerides, which can be used later by the body for energy,” said Dr. Lauri Wright, a registered dietitian, member of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, and an assistant professor of nutrition at the University of South Florida.
Most of the fats we eat, such as natural oils both polyunsaturated and monounsaturated animal fats and trans fats, are triglycerides. While both healthy and unhealthy fats contribute to triglyceride levels, trans fats like margarine and saturated fats like fatty red meats, poultry skin, lard and some full-fat dairy products can elevate triglyceride levels more than leaner cuts of meat and unsaturated fats like olive oil, avocados, nuts and low-fat dairy products. Refined, simple carbohydrates and alcohol can also increase triglyceride levels, said Wright.
High triglyceride levels can also be a side effect of medications like beta blockers, birth control pills, steroids and diuretics, according to the Mayo Clinic.
Also Check: Is Tuna Good For High Cholesterol
Not Necessarily A Cure
Fish oil may not be a cardiovascular event cure-all, according to a study published in JAMA and recently presented at the American Heart Associations Scientific Sessions 2020. In the study, the researchers assessed omega-3 carboxylic acids or omega-3 CA , a medication that is derived from fish oil.
The STRENGTH trial, which began in 2014, encompassed data from 13,078 adults at 675 centers in 22 countries.
All of the patients were being treated with statins and had known heart, brain, or leg artery blockages. They were at a higher risk for heart disease due to factors such as smoking and diabetes. The subjects either took the omega-3 CA medication or a placebo. The placebo used was corn oil.
The team compared the rates of cardiovascular death, heart attack, stroke, need for stenting or bypass surgery, and hospitalization for unstable angina in all of the study participants.
The study found that a combination of eicosatetraenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid omega-3 fatty acids found in certain fishdid not lower major cardiac events in high-risk patients.
The researchers found that 1,580 patients experienced at least one cardiac event. There were not any significant differences in cardiac event risk between participants in one group versus the other. However, the researchers did find that people taking the omega-3 CA medication developed atrial fibrillation more frequently than those who took corn oil.
Reconfiguring Cholesterol Metabolism As Host Response To Infection
The interdependence of innate immune signaling processes and the regulation of sterols and fatty acid metabolism is increasingly being consolidated through emerging data . Their role in production of inflammatory mediators has been reported by several groups . Interferons modulate the expression of a multitude of IFN-stimulated genes including viperin, which has been observed to be highly upregulated in response to bacterial LPS, double-stranded DNA, and RNA analogs, and also possesses antiviral activity against a range of viruses including HCV and dengue virus . In a similar vein, inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis also exerts an antiviral effect . SREBPs are involved in coordinating the regulation of the sterol and fatty acid biosynthesis pathways IFNs effectively inhibit SREBP2 at both mRNA and protein levels. Interestingly, WNV-induced redistribution of cellular cholesterol was found to downregulate IFN-stimulated JAKSTAT antiviral signaling response to infection, potentially by removing cholesterol from their usual microenvironment.
You May Like: Are Egg Beaters Low In Cholesterol
Do They Have A Direct Relationship With Cholesterol
As there are mixed reviews on how omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids affect cholesterol, its best to lay out all the knowledge and findings out there. While the American Heart Association and Heart Foundation, claim that consuming polyunsaturated fats help increase HDL levels and lower LDL levels , it may be the case that not all polyunsaturated fats are considered equal. According to the International Food Information Council Foundation, omega-3 fatty acids decrease serum triglyceride and total cholesterol levels, and may increase or have no effect on high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol, while diets high in omega-6 fatty acids are associated with lower blood levels of total cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol, but also with lower blood levels of the protective HDL cholesterol. Overall, this means that our bodies may be out of sync in our omega-3 to omega-6 balance. Omega-3 seems to have a better outlook for healthy HDL levels than omega-6, which focus more on LDL levels.
What Are Trans Fatty Acids
Trans fatty acids are formed when a liquid fat is changed into a solid fat through a process called hydrogenation. Many manufacturers use hydrogenated fats in their ingredients because it creates a product with an extended shelf life and better consistency.
Trans fatty acids are especially bad for you. They raise the levels of LDL cholesterol in your blood and lower the levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
There are currently no safe levels of trans fat to consume each day, so avoid them completely or eat them as little as possible.
Many manufacturers have stopped using or greatly reduced the amount of trans fats in their foods. But, check the label and avoid:
Don’t Miss: How Often To Check Cholesterol
Fat Saturation And Ldl Receptors
Many studies have shown that dietary fatty acids regulate plasma LDL-C levels by affecting LDL receptor activity, protein, and mRNA abundance .
Mustad et al. demonstrated that dietary SFA markedly decreased LDL receptor protein levels in pigs fed a diet containing 0.25% cholesterol, compared to pigs fed a diet with cholesterol only or to controls fed a low-fat, cholesterol-free diet. In contrast, pigs fed a diet high in PUFA had increased LDL receptor levels compared to pigs fed a diet with cholesterol only or a low-fat, cholesterol-free diet . These distinct effects of dietary fatty acids were accompanied by parallel changes in LDL receptor mRNA levels. These data provide strong evidence for an independent and positive effect of PUFAs on the regulation of LDL receptor expression. It is important to note that these differential effects of dietary fatty acids were observed only in pigs fed the lowest level of dietary cholesterol, suggesting that high cholesterol intake has a dominant and repressive effect on LDL receptor mRNA levels that cannot be alleviated by fatty acids.